- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
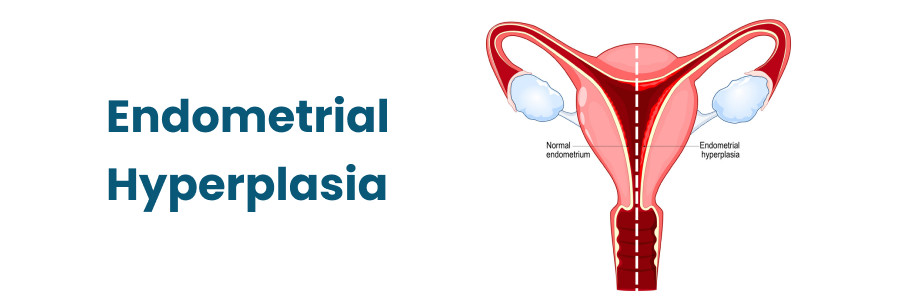
Endometrial Hyperplasia: What Women Should Know
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where the lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium, becomes unusually thick. This happens because of an overgrowth of cells, often due to an imbalance of hormones, specifically estrogen and progesterone. While it can be concerning, early detection and proper management can significantly improve outcomes.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhat Causes Endometrial Hyperplasia
The primary cause of endometrial hyperplasia is an excess of estrogen without enough progesterone to counterbalance it. Several factors can contribute to this hormonal imbalance:
- Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can lead to an increase in estrogen.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can produce additional estrogen.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This condition often leads to irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Using estrogen without progesterone can increase the risk.
- Certain Medications: Some treatments for breast cancer, like Tamoxifen, can influence estrogen levels.
Symptoms of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Recognizing the symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding: This can include heavy periods, bleeding between periods, or periods that last longer than usual.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Any bleeding after menopause should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Pelvic Pain: Some women may experience discomfort or pain in the pelvic area.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis can prevent the progression of the condition and reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosing Endometrial Hyperplasia
Medical History and Physical Exam
Your doctor will start by taking a thorough medical history and conducting a physical exam. This helps in understanding your symptoms and identifying potential risk factors.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound is often the first imaging test performed. It helps to measure the thickness of the endometrium and can provide initial clues about the presence of hyperplasia.
Endometrial Biopsy
An endometrial biopsy involves taking a small sample of the endometrial tissue for examination under a microscope. This is the most definitive way to diagnose endometrial hyperplasia and determine if there are any abnormal or precancerous cells.
Hysteroscopy
During a hysteroscopy, a thin, lighted tube is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. This allows the doctor to look inside the uterus and take a biopsy if necessary.
Treatment Options for Endometrial Hyperplasia
Treatment for endometrial hyperplasia depends on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the patient's overall health and desire for future pregnancies.
Hormonal Therapy
- Progestin Therapy: This involves taking progestin, a synthetic form of progesterone, to help balance the effects of estrogen and reduce the thickness of the endometrium.
- Hormonal IUD: A hormonal intrauterine device ( IUD) can release progestin directly into the uterus, which can be effective in treating hyperplasia.
Surgical Options
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): This procedure involves scraping away the excess endometrial tissue. It can provide immediate relief from symptoms and help with diagnosis.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, especially if cancerous cells are found, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended.
Lifestyle Changes and Monitoring
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help balance hormone levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments and regular ultrasounds or biopsies may be necessary to monitor the condition and ensure that it does not progress.
Managing Endometrial Hyperplasia
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your gynecologist are essential for managing endometrial hyperplasia. These visits allow for ongoing monitoring and early detection of any changes in the condition.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing endometrial hyperplasia. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy weight and balance hormones.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can aid in weight management and overall health.
- Avoiding Excess Estrogen: Limit the use of medications or supplements that increase estrogen levels without balancing progesterone.
Seeking Care at Medicover Hospitals
Medicover Hospitals offer care for women with endometrial hyperplasia. Our team of experienced gynecologists and healthcare professionals are equipped with diagnostic tools and treatment options to provide personalized care.
Why Choose Medicover Hospitals?
- Expert Team: Our specialists have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating endometrial hyperplasia.
- Advanced Technology: We use the latest technology for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Patient-Centered Care: We prioritize patient comfort and ensure that each treatment plan is tailored to meet individual needs.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentConclusion
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and potential health risks if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your reproductive health, don't hesitate to seek medical advice. Medicover Hospitals are here to provide the care and support you need to maintain your health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where the lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes too thick due to an overgrowth of cells.
Symptoms may include heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and sometimes abnormal discharge.
It is often caused by an imbalance in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can be influenced by hormonal changes or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Diagnosis typically involves pelvic exams, ultrasounds, and endometrial biopsies to assess the thickness of the uterine lining.
Treatments can include hormonal therapy, such as progestins, or surgical procedures if hyperplasia is severe or precancerous.

- Cardiology 2132
- Dermatology 168
- Endocrinology 135
- ENT 97
- Fertility 217
- Gastroenterology 232
- General 478
- General-Medicine 1685
- Gynecology 169
- Hematology 85
- Infectious-Diseases 208
- Neurology 207
- Oncology 345
- Ophthalmology 65
- Orthopedics 187
- Pediatrics 83
- Procedure 72
- Public-Health 209
- Pulmonology 126
- Radiology 13
- Second Opinion 311
- Urology 294
- Wellness 600
- Woman-and-child 447
- Others 10217
Related Blogs
If you have any questions, please fill out the enquiry form or call us, and we will get back to you promptly.
040-68334455