- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting means that you don't eat for a period each day or week. Some popular approaches to intermittent fasting include:
- Alternate-day fasting: Eat normally one day, then have a small meal or no food at all the next.
- 5:2 fasting: Eat on a regular diet for five days, then eat very little or fast for two days.
- Daily time-restricted fasting: Eat within an eight-hour window each day, like skipping breakfast and having lunch and dinner between noon and 8 pm
Intermittent Fasting (IF) is a popular health trend worldwide. It involves alternating between eating and fasting periods.
Although it doesn't specify what to eat, many find it effective for weight loss and simplifying their lifestyle. While adjusting may cause initial hunger, most adapt quickly. Water, coffee, tea, and non-caloric drinks are allowed during fasting, with some methods permitting small, low-calorie snacks. Supplements are generally allowed as long as they're calorie-free.
How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
Intermittent fasting involves choosing specific eating and fasting periods. For example, you might eat only for 8 hours each day and fast for the rest of the time. Another option is eating one meal a day, two days a week. There are many different schedules for intermittent fasting.
Experts say that after several hours without food, the body depletes its sugar stores and starts burning fat, a process called "metabolic switching."
In contrast, many people in the U.S. eat throughout the day. If you're eating three meals plus snacks without exercising, your body uses the calories from food instead of burning fat.
Intermittent fasting extends the time your body needs to burn through calories from your last meal and start burning fat.
What Are the Methods of Intermittent Fasting?
There are several different ways to do intermittent fasting, all of which involve dividing the day or week into periods of feeding and fasting. During periods of fasting, you eat very little or nothing at all. These are the most popular methods.
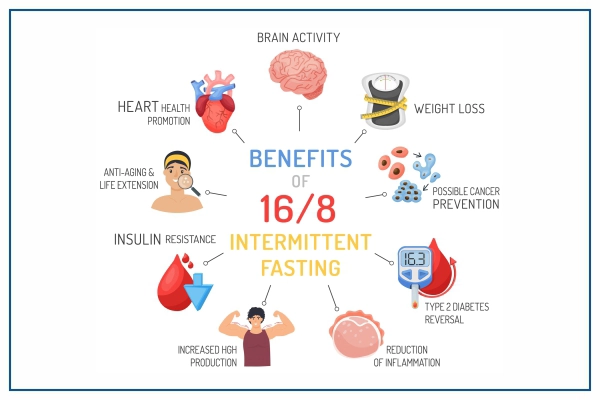
The 16/8 Method
Fasting for 16 hours and eating for 8 hours a day. People do this mainly by eliminating breakfast or dinner from their food intake; they start eating around 10 a.m. and stop eating around 6 p.m. This type of fast can help improve heart health and regulate weight.
Eat-Stop-Eat
Once or twice a week, eat nothing from dinner one day to dinner the next day (a 24-hour fast).
5:2 Diet
Eat about 1⁄4 (quarter) of your total daily caloric needs on the next two days of the week. Eat the next five days of the week as usual. Research has shown that this diet may help regulate weight and reduce the number of molecules that trigger hunger.
Alternate Day Fasting
Eat as much as you need one day and fast the next day, drinking only calorie-restricted liquids. Research has shown that this can help you achieve a healthy weight, regulate insulin and blood sugar, and reduce inflammation in the body.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Many studies have been conducted on intermittent fasting, both in animals and humans. These studies have shown that it can have powerful benefits for weight management and the health of the body and brain. It can also lead to longer life.
Here are the main health benefits of intermittent fasting:
- Weight Loss: As described above, it will help you shed weight and belly fat without actively reducing your calories.
- Insulin Resistance: Fasting can reduce insulin resistance, lowering blood sugar by 3% to 6% and fasting insulin levels by 20% to 31%, which should protect against type 2 diabetes.
- Inflammation: Some studies show reductions in inflammation markers, a critical factor in many chronic diseases.
- Heart Health: It can lower "bad" LDL cholesterol, blood triglycerides, inflammatory markers, blood sugar, and insulin resistance, all risk factors for heart disease.
- Cancer: Some studies have shown that alternate-day fasting can reduce the risk of cancer by slowing the development of lymphoma, limiting tumour survival, and slowing the spread of cancer cells.
- Brain Health: Fasting increases the BDNF hormone in the brain, which can help the growth of new nerve cells and protect against Alzheimer's disease.
- Anti-Aging: Fasting can extend rats' lifespans. Studies have shown that fasted rats live 36% to 83% longer.
Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting is an easy and flexible way to lose weight. Studies show it can help you shed pounds and improve your health. By eating less, you naturally consume fewer calories, which leads to weight loss.
There are several things to keep in mind if you want to lose weight:
- Food Quality: The food you eat is still important. Try to eat mostly whole, single-ingredient food.
- Consistency: As with any other weight-loss method, it needs to be used for a long time for it to work.
- Patience: It may take your body some time to adjust to the protocol. Try to be consistent with your meal schedule, and it will be easier.
Intermittent Fasting and Thyroid
Fasting can affect your thyroid hormones, but they usually bounce back after you eat. Different types of meals can impact this differently.
- After fasting, people are affected by the recovery of thyroid hormones.
- Those who ate pure carbohydrates saw their T3 return to normal.
- Those who ate mixed fat, carbohydrate, and protein meals saw their T3 return to normal.
- Those who ate only protein still had lower T3.
- Those who ate only fat still had lower T3.
Despite these results, several studies have shown that thyroid hormones return to pre-fast values after a short break with a meal, suggesting that extended fasting may not be detrimental to humans.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentIntermittent Fasting and Heart Health
Fasting might have benefits for your heart, like improving cholesterol levels and sugar metabolism. But more research is needed to be sure. Eating healthy and staying active are also crucial for a healthy heart.
What are the Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting:
- Hunger and Cravings: Feeling hungry, especially at the start.
- Fatigue: Low energy or tiredness during fasting.
- Headaches: Common during the adjustment period.
- Irritability: Mood swings or irritability from hunger.
- Digestive Issues: Constipation, bloating, or nausea.
- Sleep Disruption: Fasting may affect sleep patterns.
- Nutrient Deficiency: Risk of missing essential nutrients if not eating balanced meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
According to a 2014 review, intermittent fasting reduced body weight by 3 to 8% for 3 to 24 weeks.
In a review of studies on intermittent fasting and alternate-day fasting, people experienced a 4 to 7% decrease in abdominal fat in 6 to 24 weeks.
Consider a simple form of intermittent fasting. Limit the hours of the day that you eat, and for the best effect, eat earlier in the day (between 7 a.m. and 3 p.m., or even between 10 a.m. and 6 p.m. p.m., but not at night before bed). Evette snacking or eating at night all the time.
Intermittent fasting can increase the metabolism of your thyroid medications. It also affects the way your body uses its energy.
Fasting can lead to an electrolyte imbalance. This can make the heart unstable and vulnerable to arrhythmias.
Intermittent fasting is associated with lower rates of heart failure and a longer lifespan.

- Cardiology 2132
- Dermatology 168
- Endocrinology 135
- ENT 97
- Fertility 217
- Gastroenterology 232
- General 478
- General-Medicine 1685
- Gynecology 169
- Hematology 85
- Infectious-Diseases 208
- Neurology 207
- Oncology 345
- Ophthalmology 65
- Orthopedics 187
- Pediatrics 83
- Procedure 72
- Public-Health 209
- Pulmonology 126
- Radiology 13
- Second Opinion 311
- Urology 294
- Wellness 600
- Woman-and-child 447
- Others 10217
Related Blogs
If you have any questions, please fill out the enquiry form or call us, and we will get back to you promptly.
040-68334455