- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
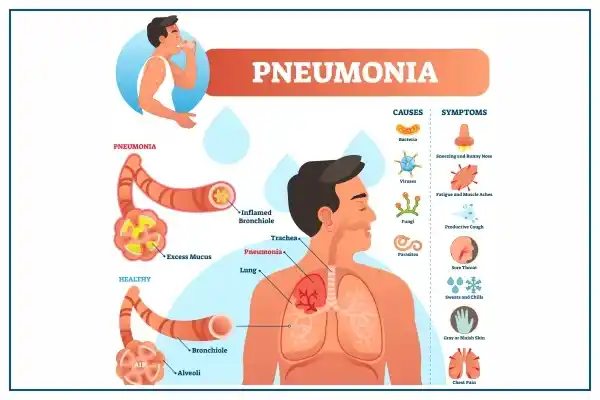
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a lung infection ranging from mild to severe, often requiring hospitalization. It occurs when infections fill the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) with fluid or pus, making it hard to breathe and absorb oxygen into the bloodstream. Babies younger than 2 and people older than 65 are at higher risk due to weaker immune systems.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
Yes, the germs causing pneumonia are contagious. Both viral and bacterial pneumonia can be spread by inhaling airborne droplets from sneezing or coughing or by touching contaminated surfaces. Fungal pneumonia, however, is not passed from person to person.
How Does Pneumonia Spread?
Pneumonia spreads through airborne droplets when someone coughs or sneezes. You can also get it by touching surfaces they have touched or using their tissues.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionSymptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Coughing up greenish, yellow, or red mucus
- Fever, sweating, and chills
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Sharp chest pain worsened by deep breathing or coughing
- Loss of appetite, low energy, and fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting, especially in young children
- Confusion, especially in older adults
Causes of Pneumonia
Bacterial Pneumonia:
- Caused by different bacteria, mainly Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Often occurs when the body is weakened by illness, poor nutrition, or a weakened immune system.
Viral Pneumonia:
- Caused by various viruses, including the flu (influenza), responsible for about one-third of all pneumonia cases.
- Viral pneumonia can increase the likelihood of bacterial pneumonia.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia:
- Referred to as atypical pneumonia, caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Generally causes mild, widespread pneumonia affecting all age groups.
Other Pneumonia:
- Less common cases caused by other infections, including fungi.
Is Pneumonia Curable?
Many cases of pneumonia can be cured with proper recognition and treatment.
Bacterial Infections:
Early discontinuation of antibiotics can lead to the recurrence and contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Viral Pneumonia:
Often resolves in one to three weeks with home treatment. Antivirals may be needed in some cases.
Fungal Pneumonia:
Treated with antifungal medications, which may require a longer period of treatment.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentDiagnosis of Pneumonia
Your doctor will start by asking about your symptoms and medical history and will listen to your lungs. Tests may include:
- Chest X-ray to find the infection in your lungs.
- Pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen levels.
- Sputum test to check the fluid in your lungs for infection.
If your symptoms started in the hospital or if you have other health problems, additional tests may include:
- Arterial blood gas test to measure oxygen.
- Bronchoscopy to check for blockages or other problems.
- CT scan for a detailed picture of your lungs.
- Pleural fluid culture to look for bacteria.
Treatments for Pneumonia
Treatment depends on the type of pneumonia, the germ causing the infection, and its severity.
Bacterial Pneumonia:
Treated with antibiotics. It's important to take them as prescribed.
Viral Pneumonia:
Antiviral medication may be prescribed. Recovery typically takes one to three weeks.
Severe Cases:
May require hospitalization, oxygen therapy, or IV antibiotics.
Risk Factors for Pneumonia
Anyone can get pneumonia, but some people are at higher risk:
- Children and newborns with immature immune systems
- Older adults with weakened immune systems
- Pregnant women
- People on immune-suppressing medications
- Individuals with diseases that weaken the immune system (e.g., cancer, HIV, AIDS)
- People with autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
- Those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis (CF), or asthma
People at risk should be especially careful around those who have recently had pneumonia or another respiratory infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Children under the age of 2 are at risk because their immune systems are still developing, and adults over 65 are at higher risk because, as we age, our immune systems slow down in responding to infection.
Viral pneumonia usually goes away on its own. Therefore, treatment focuses on alleviating some of the symptoms. A person with viral pneumonia should get enough rest and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
Pneumonia can range from mild to severe or life-threatening infection and can sometimes lead to death.
Pneumonia can be contagious for 2-14 days. Generally, the goal of medicines given for pneumonia is to limit the spread of the disease. A person with bacterial pneumonia will stop being contagious within two days after taking antibiotics.
Surprisingly, even with severe pneumonia, the lung usually recovers and has no lasting damage, although occasionally, there may be some scars on the lung (rarely leading to bronchiectasis) or on the surface of the lung (the pleura).
First-line antibiotics that might be selected include the macrolide antibiotics azithromycin (Zithromax), clarithromycin (Biaxin XL) or the tetracycline doxycycline.
Some viruses that cause colds and flu can cause pneumonia. Viruses are the most common cause of pneumonia in children younger than 5 years old. Viral pneumonia is usually mild, but in some cases, it can become very serious.

- Cardiology 2132
- Dermatology 168
- Endocrinology 135
- ENT 97
- Fertility 217
- Gastroenterology 232
- General 478
- General-Medicine 1685
- Gynecology 169
- Hematology 85
- Infectious-Diseases 208
- Neurology 207
- Oncology 345
- Ophthalmology 65
- Orthopedics 187
- Pediatrics 83
- Procedure 72
- Public-Health 209
- Pulmonology 126
- Radiology 13
- Second Opinion 311
- Urology 294
- Wellness 600
- Woman-and-child 447
- Others 10217
Related Blogs
If you have any questions, please fill out the enquiry form or call us, and we will get back to you promptly.
040-68334455