- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
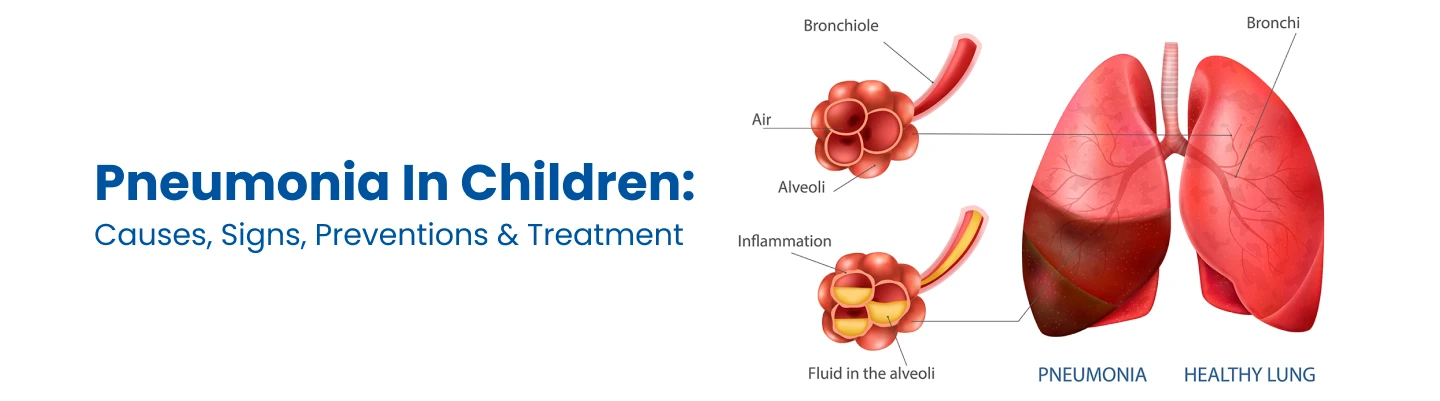
Pneumonia in Children: Overview
Pneumonia in children is spread by infected people who carry the germs in droplets of liquid in their throat, nose, or mouth. The infected person coughs up germs in the air. Your child inhales the germs or comes into direct contact with the saliva or mucosa of the infected person by touching something.
Pneumonia occurs most often during cold months when children spend most of their time indoors in close contact with other people.
Children under the age of 2 are at the highest risk of pneumonia. Almost everyone makes a full recovery with proper medical care.
Symptoms of Pneumonia in Children
Pneumonia in children manifests with various symptoms, which can differ based on the type and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
Prompt medical attention is crucial if these symptoms occur, especially in younger children who may be more vulnerable.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionTypes of Pneumonia in Children
Pneumonia in children can be categorized into several types, each caused by different pathogens:
- Bacterial Pneumonia : Caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, this type of pneumonia typically presents with sudden onset symptoms such as productive cough, chest pain, and high fever.
- Viral Pneumonia : Viruses such as Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Influenza virus, and others can lead to viral pneumonia, characterized by symptoms similar to bacterial pneumonia but with a slower progression and potential respiratory complications.
- Mycoplasma Pneumonia : This type is caused by Mycoplasma bacteria and often affects older children, presenting with mild symptoms that can include persistent cough and fatigue.
Pneumonia in Children Treatment
Treatment for pneumonia in children varies based on the type and severity of the infection. Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may resolve with rest, fluids, and supportive care to alleviate symptoms. It's essential to follow the doctor's recommendations for medication and monitor closely for any signs of improvement or worsening.
Causes of Pneumonia in Children
Children can develop pneumonia due to infections caused by:
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Other microbes
Common causes include respiratory infections like:
- The flu or colds
- Exposure to environmental irritants
- Pollutants
and in some cases, aspiration of food or liquids into the lungs.
Common Cause of Pneumonia in Children
The most frequent causes of pneumonia in children are viral and bacterial infections, particularly viruses like RSV and influenza during colder months. Bacterial pneumonia often follows respiratory tract infections and can be caused by various bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentDiagnosis for Pneumonia in Children
Diagnosing pneumonia in children involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Tests may include chest X-rays to assess lung involvement, blood tests to detect infection markers, and occasionally sputum cultures or other specialized tests to identify the specific pathogen causing the infection.
Prevention of Pneumonia in Children
Preventing pneumonia in children involves several strategies, including vaccination against common pathogens like pneumococcal and influenza.
Good hygiene practices such as frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding exposure to smoke or other pollutants can also reduce the risk of infection.
Is Pneumonia Contagious?
While pneumonia itself is not contagious, the viruses and bacteria that cause it can spread from person to person through respiratory droplets.
Close contact with an infected person, sharing utensils or personal items, and inadequate hand hygiene can contribute to the transmission of pneumonia-causing pathogens.
Conclusion
Pneumonia in children is a serious respiratory infection that can range from mild to severe. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt medical treatment, and preventive measures such as vaccinations and good hygiene practices are crucial in managing and preventing pneumonia.
By understanding the different types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options, parents and caregivers can effectively support children's respiratory health and reduce the risk of complications associated with pneumonia.
Frequently Asked Questions
Signs of pneumonia in children may include high fever, rapid or difficulty breathing, coughing, chest pain, fatigue, and vomiting. If your child exhibits these symptoms, especially after a cold or flu, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and diagnosis.
Danger signs of pneumonia in children include severe difficulty breathing, bluish lips or nails, lethargy, dehydration, persistent fever, chest pain, and coughing up blood. Seek immediate medical attention if your child shows any of these symptoms.
The treatment for pneumonia in children depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. It may include antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, antiviral medication for viral pneumonia, supportive care such as rest, fluids, and fever-reducing medicines, and, in severe cases, hospitalization for oxygen therapy or intravenous fluids.
With prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most children recover fully from pneumonia. Antibiotics or antiviral medications help eliminate the infection, and supportive care aids in symptom relief. However, recovery time varies depending on the severity of the illness and the overall health of the child.
Mild pneumonia usually goes away in 2 to 3 weeks. A severe case of pneumonia may take 6 to 8 weeks or more to recover. Rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, healthy food, and plenty of fluids will help your child heal at home.
A diet rich in protein is beneficial for people with pneumonia. Foods like nuts, seeds, beans, white meat, and cold-water fish like salmon and sardines have anti-inflammatory properties, which are suitable for pneumonia.

- Cardiology 2132
- Dermatology 168
- Endocrinology 135
- ENT 97
- Fertility 217
- Gastroenterology 232
- General 478
- General-Medicine 1685
- Gynecology 169
- Hematology 85
- Infectious-Diseases 208
- Neurology 207
- Oncology 345
- Ophthalmology 65
- Orthopedics 187
- Pediatrics 83
- Procedure 72
- Public-Health 209
- Pulmonology 126
- Radiology 13
- Second Opinion 311
- Urology 294
- Wellness 600
- Woman-and-child 447
- Others 10217
Related Blogs
If you have any questions, please fill out the enquiry form or call us, and we will get back to you promptly.
040-68334455