- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
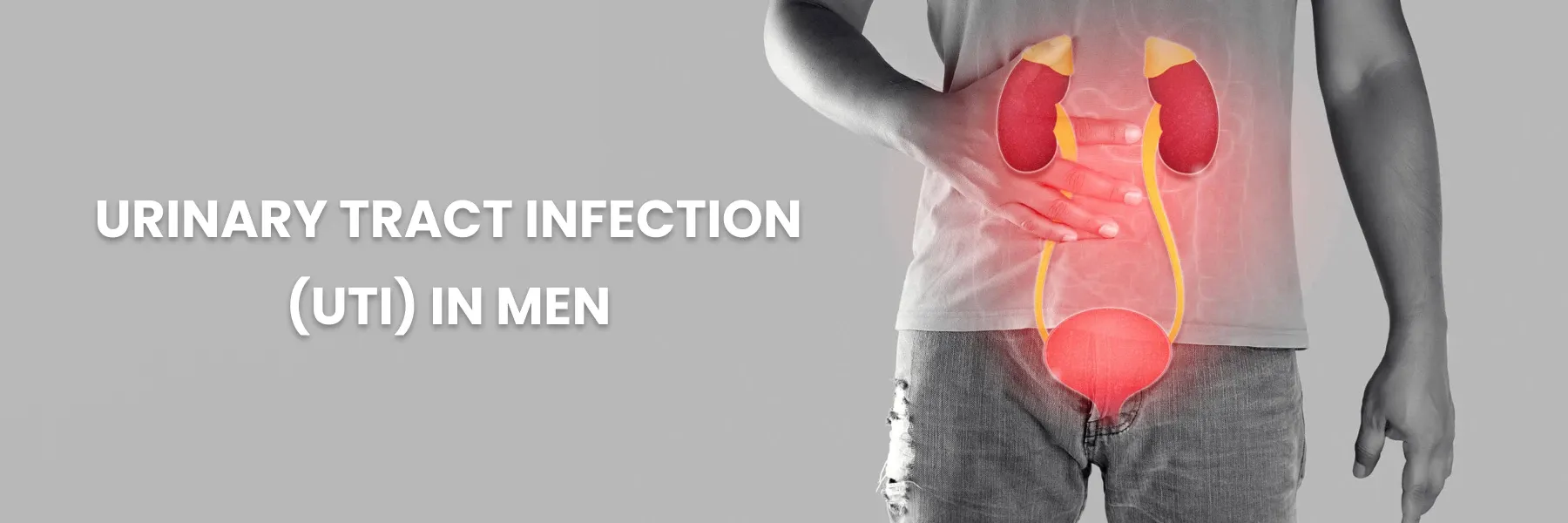
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections affecting the urinary tract when bacteria enter through the urethra. While less common in men, UTIs can lead to significant health issues.
Our comprehensive guide covers all the essential aspects of UTIs in males, from understanding risk factors to effective prevention tips and home remedies like cranberry supplements and increased fluid intake.
What is Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that occur when bacteria, often from the rectum or skin, enter the urinary tract through the urethra. While UTIs can affect various parts of the urinary tract, bladder cystitis is the most frequent.
What is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Men?
Although Urinary Tract infections (UTIs) are more common in women, men are also susceptible. Despite being less frequent, UTIs in men can lead to significant health issues and discomfort. UTIs are more prevalent in older males. The prostate surrounds the neck of the bladder where the urethra connects.
Enlargement of the prostate can narrow the bladder neck, obstructing the flow of urine. This obstruction can lead to the retention of bacteria in the bladder, increasing the risk of UTIs.
What are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections in Men?
- Frequent urination
- Low-grade fever
- Hematuria (urine containing blood)
- Solid or persistent urge to urinate
- Cloudy urine with a strong odor
- Tingling or burning sensation during or after urination
- Difficulty urinating, especially with prostate conditions
What are the Risk Factors for UTIs in Males?
- UTIs are commonly caused by Escherichia coli (E.coli), a natural bacterium in the body.
- Infections can affect various parts of the urinary tract: kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
- Lower-tract infections: urethritis and bladder infections.
- Upper tract infections: ureter and kidney infections.
- The urethra, through which urine is expelled via the penis, is the entry point for microorganisms into the urinary tract.
Factors Increasing UTI Risk
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Urinary tract obstructions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate
- Recent urinary tract or kidney surgery
- Inadequate fluid intake
What Methods are Used to Diagnose an Urinary Tract Infection?
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men includes;
Medical History and Symptoms Assessment
- Healthcare providers inquire about medical history and UTI symptoms.
- Sexual history may be discussed due to its relevance in UTI development.
Diagnostic Tests
- Urine Analysis: Lab analysis of urine to detect infection.
- Physical Examination: Examination of discharge from the urethra and prostate organs.
- Prostate Exam: Recommended if prostate-related issues are suspected.
Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound or X-ray: Provides detailed images of the urinary tract if necessary.
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): Specialized X-ray to visualize bladder, ureters, and kidneys.
- Cystoscopy: Procedure to examine urethra and bladder interiors using a small, illuminated instrument, typically performed by a urologist.
Treatment Options for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men
Antibiotic Therapy
- Oral antibiotics are the standard treatment for UTIs.
- The choice of antibiotic depends on the bacteria causing the infection and the site affected.
Duration of Treatment
- Lower urinary tract infection: Typically treated with antibiotics for up to one week.
- Upper tract infection: May require antibiotic treatment for up to two weeks.
Severe Cases
Hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics if the infection causes fever, severe pain, vomiting, or a significant kidney infection.
Duration of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Cure
With Treatment
- Symptoms typically improve within 24 hours of starting antibiotic treatment.
- Complete the entire course of prescribed medication to prevent reinfection.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentWithout Treatment
- Untreated UTIs can persist for an extended period.
- Risks include kidney and bladder damage and, in severe cases, bloodstream infection (sepsis), which can be life-threatening.
Prevention Tips for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men
Maintain Healthy Fluid Intake
Drink at least 50 ounces (approximately 1.5 litres) of fluids daily, particularly water, to keep bladder tissue healthy and dilute urine, reducing bacteria concentration.
Regularly Empty Your Bladder
Ensure you empty your bladder frequently, ideally four to eight times daily, to prevent bacteria from multiplying in stagnant urine.
Urinate Immediately After Sexual Activity
Voiding immediately after sexual activity helps flush out bacteria introduced into the urethra during intercourse, reducing the risk of infection.
Consider Cranberry Supplements
While scientific evidence on cranberry supplements preventing UTIs is inconclusive, they may offer benefits by reducing bacterial adhesion. Opt for concentrated supplements over sugary cranberry juice.
What Are Some Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infections in Men?
Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men
Cranberry Products
Cranberry juice or concentrated supplements may help prevent UTIs by reducing bacterial adhesion in the urinary tract.
Bearberry (Uva Ursi)
Bearberry, also known as uva ursi, is sometimes used for its potential antibacterial properties that could help treat UTIs.
Increased Fluid Intake
Drinking plenty of water and fluids helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and promotes overall urinary health.
Probiotics
Probiotics containing lactobacillus may help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract.
Avoiding Irritants
Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners can help reduce irritation of the urinary tract.
Frequently Asked Questions
While not all urinary tract infections are preventable, the following simple precautions can significantly reduce your likelihood of developing one:
- Fluidly consume water.
- Immediately empty your bladder and proceed to the restroom when you sense the need to do so.
- Use a condom during sexual activity.
- Urinate immediately after sexual activity.
- Observe proper genital sanitation.
- When showering or bathing, cleanse beneath the foreskin if you are not circumcised.
UTIs are primarily caused by bacterial infections, with E. coli being the most common. In males, infections are often caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and anal intercourse. Urinary system obstructions like kidney stones or benign prostatic hyperplasia can cause upper-tract infections. Urinary catheterisation is a potential risk factor for UTIs in males. Other risk factors include diabetes, dehydration, urinary tract surgery, lack of circumcision, and incontinence.
Over fifty percent of women will develop a urinary tract infection at some point, considerably more probable than men.
he urethra in females is shorter than that of males and is located in closer proximity to the anus, the site of stool expulsion. Additionally, it is in close proximity to the vagina, an area that can accumulate pathogens during sexual activity. Bacteria from the anus or vagina have easy access to a woman's urinary tract due to this position, which facilitates the development of infections.
Additionally, he asserts that postmenopausal women may experience hormonal-induced vaginal changes that increase their susceptibility to infections. However, this condition is treatable with medications available by prescription.
Urinary tract infection in men may, in fact, contribute to significant complications. If left untreated, the infection may persist for an extended period of time. If left untreated, the disease can cause irreversible harm to the kidneys and bladder, or it can travel to the bloodstream. If it enters the bloodstream, the infection is potentially fatal.
The standard treatment for urinary tract infections is a course of antibiotics. Prescription medication is necessary to prevent the spread of the invasive bacteria to other areas of the body and to neutralise it.
When treatment is initiated, the majority of UTI symptoms resolve within twenty-four hours. Reinfection may ensue from the prolonged discontinuation of medication prior to the intended conclusion of treatment. Without treatment, the infection could remain for a prolonged period. It is potentially fatal if untreated, as it can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys and bladder and enter the circulation.
Dietary adjustments for a urinary tract infection (UTI) entail introducing and excluding specific foods and beverages. Sugar should be avoided. The following are additional foods and beverages to avoid while suffering from a UTI:
- Spicy dishes.
- Citrus fruits such as grapefruits, oranges, lemons, and limes are high in vitamin C, which can boost the immune system. However, they can also irritate the bladder and exacerbate UTI symptoms.
- Caffeinated beverages.

- Cardiology 2132
- Dermatology 168
- Endocrinology 135
- ENT 97
- Fertility 217
- Gastroenterology 232
- General 478
- General-Medicine 1685
- Gynecology 169
- Hematology 85
- Infectious-Diseases 208
- Neurology 207
- Oncology 345
- Ophthalmology 65
- Orthopedics 187
- Pediatrics 83
- Procedure 72
- Public-Health 209
- Pulmonology 126
- Radiology 13
- Second Opinion 311
- Urology 294
- Wellness 600
- Woman-and-child 447
Related Blogs
If you have any questions, please fill out the enquiry form or call us, and we will get back to you promptly.
040-68334455