Enzyme Linked Immunoassay (ELISA) Test: Types, Cost and Procedure
The enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) is used to identify antibodies in the blood produced by a harmful substance that has entered the body. This test is widely used to detect blood-borne viruses like HIV, HBV, HCV, and HTLV.
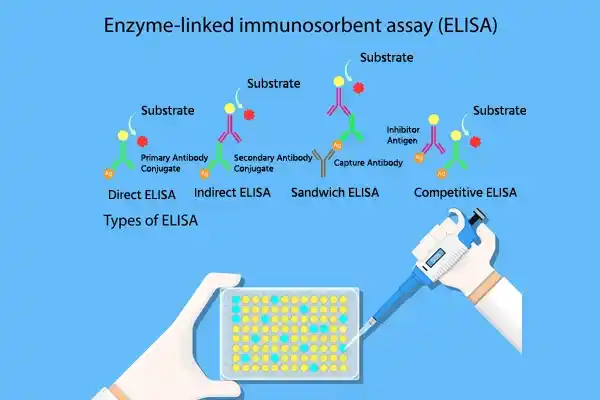
Types of ELISA
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a test that detects and measures proteins, antibodies, and hormones. There are four main types of ELISA shows, every single one with Lego designs and applications:
Direct ELISA
In a direct ELISA, the antigen attaches directly to the surface of the test well. The next step is to introduce a primary antibody that is linked with an enzyme and specific for the target antigen, which directly binds to the antigen. The antibody is further introduced with a substrate that reacts with the enzyme and gives a detectable colour change. The procedure is simple and rapid, offering fewer steps than other types of ELISA but usually less sensitive.
- Use: Most often used in simpler samples for antigen detection
- Pros: More efficient and less complex.
- Cons: Less sensitivity is caused by lower signal amplification.
Indirect ELISA
An indirect ELISA uses two antibodies to detect a target antigen. The antigen is coated initially on the plate, and then a primary antibody specific to the antigen is added. Next, an enzyme-linked secondary antibody specific to the primary antibody is added. This secondary antibody amplifies the signal to improve the assay's sensitivity.
- Use: Commonly employed for more antibodies (such as viral infections).
- Pros: it is more sensitive and more flexible due to signal amplification.
- Cons: Additional antibody step lengthens the process
Sandwich ELISA
The Married ELISA capture antibody is first attached to the healthy surface to bind to the target antigen. Once the antigen binds, an enzyme-linked specific "detection" antibody is added that also sticks to the antigen creating a "sandwich" around it. The technique involves the addition of a substrate that results in colour change based on the quantity of antigen.
- Use: For complex samples and detection of a particular antigen (such as cytokines, growth factors)
- Pros: Double binding leads to increased specificity and sensitivity
- Cons: Needs matched pairs of antibodies and nicer reagents.
Competitive ELISA
For Competitive ELISA, a known concentration of labelled antigen competes against the sample antigen for binding sites on a specific antibody. A lower colour change results from the less labelled antigen binding to the well, which occurs when there is more target antigen. This inverse relationship enables the quantitation of target antigens in biological samples.
- Use: Sensitive detection of small molecules/antigens in complex samples ( hormones, drugs)
- Pros: Useful for small molecules or low abundance targets.
- Cons: More complicated and needs exact handling for precise results.
The selection of the ELISA type entirely depends on sensitivity, specificity, sample diversity and target molecule.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
Elisa Test Cost or Price in India
ELISA Test Procedure
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) this is a laboratory technique used to detect the presence of an antigen or antibody in a sample. From the ELISA test procedure to benefits, here's what you need to know:
Sample Preparation
The sample—blood, urine, or another type of body fluid—is processed and placed in wells of a microplate that features an antigen or antibody to which it will bind.
Primary antibody/antigen addition
In direct or indirect ELISA, a target-specific primary antibody is provided. A sandwich ELISA is one in which the well is first coated with a capture antibody that binds the target antigen from the sample.
Washing the Plate
The plate is then washed to remove unbound material. This step is important for filtering out background noise and ensuring the accuracy of the test
Adding an Antibody that is Linked to the Enzyme
For indirect and sandwich ELISAs, an enzyme-linked secondary antibody is then added, and it binds to the primary antibody (in a direct ELISA, it will bind directly to the antigen).
Addition of Substrate
Substrate for the specific enzyme introduced. The enzyme acts on a substrate and causes the colour change. The strength of this colour is relative to the amount of target antigen or antibody in the sample.
Reading the Results
The intensity of the colour is measured using a spectrophotometer or plate reader and compared to the standard to calculate the amount of target molecule in the sample.
Advantages of the ELISA Test
SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY AT A HIGH LEVEL
The ELISA assay has high specificity and can detect low levels of antibodies or antigens.
Quantitative
With quantitative data from ELISA, concentrations of antigen or antibody can be accurately given.
Versatility
Wattle is the technique; it is commonly used for parts of proteins and blood, so it can produce an intensive range of data from how much virus or light count in the phase to create a vast, expensive package like Proteins Blood humping.
Speed and Efficiency
It is a rapid, large-scale, and high-throughput screening test that is recommended for diagnostic and research purposes.
Cost-Effectiveness
That helps ELISAs be the workhorses of labs worldwide because they are quite simple, relatively inexpensive, and accessible.
The ELISA test is a clinically significant diagnostic tool designed to determine the presence of an antigen in bodily fluids and effusions.
**Note: ELISA test costs in India at different locations may vary.
Book a ELISA test at Medicover Hospitals. Call us at 040-68334455
How to Prepare for an ELISA Test?
Fasting:
Check if fasting is required; some tests may require 8-12 hours of fasting.
Medication Instructions:
- Consult your doctor regarding your current medications; some may need to be paused or adjusted.
- Bring a comprehensive list of all medications, supplements, and vitamins you are taking, including dosages and frequency.
Avoid Certain Substances:
- Refrain from consuming caffeine and alcohol for at least 24 hours before the test.
- Do not use tobacco products on the day of the test.
Hydration:
Ensure you drink plenty of water before the test to stay hydrated, unless instructed to fast completely.
Health Conditions:
Inform your doctor about any recent illnesses, infections, or vaccinations that could potentially affect the test results.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
After the Test
Follow Post-Test Instructions:
- Adhere to any specific aftercare instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
- Resume your normal activities and diet unless advised otherwise.
Monitor for Side Effects:
Be vigilant for any adverse reactions at the blood draw site, such as excessive bruising or swelling, and contact your healthcare provider if necessary.
Findings of ELISA Test
- The ELISA test helps identify the situations that lead the immune system to produce antibodies, which the swab tests cannot quickly recognize.
- It helps find out about the viruses like HIV, HBV, HCV, and HTLV in the blood that lead the body to produce antibodies.
- You must visit a doctor for abnormal findings and get a complete diagnosis and treatment.