Ankylosing Spondylitis : Causes and Treatment
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS), also called axial spondyloarthritis, is a long-term inflammatory condition that can cause the bones in the spine (vertebrae) to fuse over time. This fusion reduces spinal flexibility, leading to stiffness and a hunched posture. When the ribs are involved, it may become challenging to take deep breaths, affecting overall comfort and mobility.
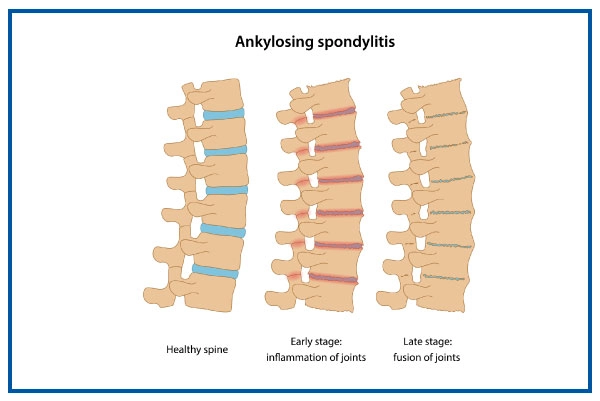
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
- Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of arthritis that causes persistent inflammation in the spine.
- The sacroiliac joints, found between the lower spine and the pelvis, become inflamed in ankylosing spondylitis.
- One of the initial signs of ankylosing spondylitis is sacroiliitis or inflammation in the joints.
- Inflammation commonly affects the joints between the vertebrae and the bones that form the spinal column, a condition known as spondylitis.
- Some individuals with ankylosing spondylitis experience severe, ongoing back pain, hip pain, and stiffness.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis symptoms often arise gradually over months or years and fluctuate with time. One of the early signs of ankylosing spondylitis that might keep you awake is lower back stiffness and pain, especially in the morning and at night. It is also possible to experience pain in the large joints, including the hips and shoulders.
- stiffness in the lower back or hips, especially in the mornings
- Poor posture/stooped shoulders/hunched-over posture
- Loss of mobility in the lower back
- Neck pain and fatigue.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhen to See a Doctor?
If you experience lower back pain that has been slowly getting worse over time, experience pain in the morning or when you are sleeping at night, it’s time to be alert. Especially if the pain gets better with activity but gets worse while you are at rest, should be discussed with your doctor.
Doctors at Medicover can help you get the right treatment and management for Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Causes of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis has no known specific cause. The inflammation can lead to new bone formation, which can lead to fusion and lasting injury. However, doctors are still unclear about why AS patients have this persistent inflammatory reaction. Both hereditary and environmental factors may contribute to AS.
Risk Factors of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis can affect anyone, but it’s more common in certain groups of people.
- Over 80% of people diagnosed with AS are under the age of 40, with most being diagnosed around 30.
- Mens are more likely to develop ankylosing spondylitis than womens.
- Having a close family member, especially a biological parent, with AS increases your risk.
- People with conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or psoriasis are also more likely to develop ankylosing spondylitis.
Complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Suffering from Ankylosing spondylitis can lead to other health issues and complications including:
- Bone deformities: New bone growth can fuse the vertebrae, limiting spinal flexibility.
- Compression fractures: Weakened bones may fracture, resulting in a stooped posture.
- Eye inflammation (uveitis): A common side effect, causing eye pain and sensitivity to light.
- Heart problems: Inflammation can affect the aorta, leading to aortic valve disease.
- Amyloidosis: In rare cases, protein buildup in organs like the heart and liver can occur.
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Although back pain is its primary symptom, AS can be difficult to identify. Since the condition affects men significantly more frequently than women, a diagnosis may be even more difficult for women. A single test to confirm AS does not exist either. The symptoms, a physical examination, and blood tests may all be used by a doctor. An MRI or an X-ray may also be performed. However, this isn't always helpful because imaging examinations may not immediately detect joint injury.
Treatments and Medication for Ankylosing Spondylitis
The symptoms, age, and overall health will all affect how you are treated. The severity of the ailment will also be a factor. Treatment aims to lessen discomfort and stiffness, avoid abnormalities and preserve a normal lifestyle as much as possible. Treatment options include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to treat inflammation and discomfort
- Tumor-necrosis-factor blockers (biologic drugs) to lessen oedema and inflammation
- DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic medications) to reduce inflammation and manage AS include sulfasalazine.
- Using corticosteroids for a brief period to lessen inflammation.
- Using muscle relaxants and painkillers for a brief period to alleviate extreme pain and muscle spasms.
- Surgery to remove a section of the thickened and hardened bone, repair a joint, or insert rods in the spine.
- Maintaining proper posture
- Regular exercising, especially back muscle strengthening routines.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Self-care and Management
Some things you do daily can help you feel better.
- Schedule some time every day, even a few minutes for an activity like swimming which improves the symptoms
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the stress on your joints. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may be of assistance. If you believe particular meals may cause changes in how you feel, look for trends.
- Avoid smoking because people who smoke frequently experience symptoms that worsen with age.
- Do massage, yoga, meditation, and counselling to reduce stress.
- While using cold on inflamed areas, apply heat to stiff joints and tight muscles.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentDos and Don’ts in Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is accompanied by pain and inflammation in the spine and pelvis. Additionally, this condition can lead to the growth and fusion of spinal segments, which causes stiffness and immobility. Although there is no permanent cure for AS, you can control your symptoms with medicines. So following the below do's, and don'ts can help you manage it.
|
Do’s |
Don’ts |
|
Exercise regularly. |
Avoid taking medicines as prescribed regularly. |
|
Avoid a sedentary lifestyle |
Fall for fad diets |
|
Avoid poor posture |
Drink too much alcohol. |
|
Eat a well-balanced diet |
Use thick pillows while sleeping |
|
Avoid chronic stress |
Lift heavy weights. |
To fight this condition, take care of yourself and keep yourself strong internally while seeking adequate medical care.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Care at Medicover
At Medicover Hospitals, we have the most trusted group of doctors and healthcare professionals who are skilled in providing the best medical treatment to our patients with compassion and care. To conduct the necessary investigations for diagnosing Ankylosing Spondylitis, our diagnostic department is equipped with advanced technology and equipment.
Our excellent team of rheumatologists, orthopedists and physiotherapists use a systematic approach to identifying and treating the condition. They provide required medical or surgical treatment as well as physical therapy to treat this condition with great precision.
Citations
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470173/Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a permanent cure for ankylosing spondylitis?
Currently, there's no permanent cure. However, treatments like medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms.
What exercises should be avoided for ankylosing spondylitis?
High-impact exercises like running or jumping, and those involving extreme bending or twisting of the spine, should be avoided.
What is the best exercise for managing ankylosing spondylitis?
Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, cycling, and gentle stretching exercises like yoga or tai chi are beneficial.
Is ankylosing spondylitis considered an autoimmune disease?
Yes, it's classified as an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks its tissues, leading to inflammation, particularly in the spine and pelvis joints.
What is the life expectancy for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis?
Although it can affect quality of life, ankylosing spondylitis typically doesn't impact life expectancy. With proper care, individuals can expect a normal lifespan.
