Celiac Disease: Causes and Treatment
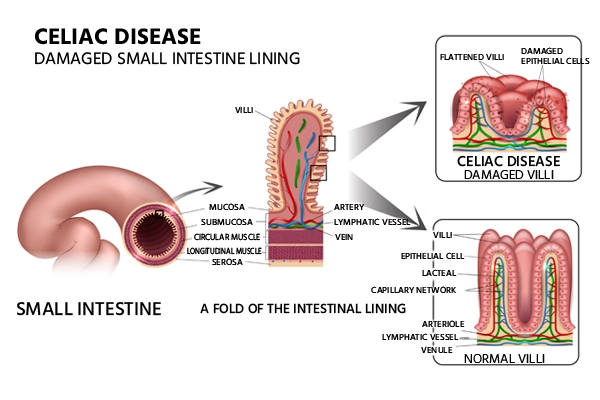
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that is induced by gluten consumption. Celiac sprue, nontropical sprue, and gluten-sensitive enteropathy are the other names for this condition. When someone with celiac disease consumes gluten, their body reacts badly to the protein, causing damage to their villi, which are small finger-like projections along the wall of their small intestine.
When the villi are damaged, the small intestine cannot absorb nutrients from food properly. This can eventually lead to malnourishment, bone density loss, miscarriage, infertility, neurological problems or certain cancers.
If the celiac disease does not improve after at least a year of no gluten, it is referred to as refractory or nonresponsive celiac disease. Most celiac disease patients are unaware of their condition. According to researchers, as few as 20% of people with the disease receive the correct diagnosis.
Celiac illness is not the same as gluten intolerance or gluten sensitivity. Gluten intolerant people may experience some of the same symptoms and choose to avoid gluten. Now let us look at the types of Celiac Disease, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment for Celiac Disease.
Types of Celiac Disease
There are different types of celiac disease:
- Classical celiac disease
- Non-classical celiac disease
- Silent celiac disease
- Potential celiac disease
- Refractory celiac disease
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionCeliac Disease Causes
The exact cause of celiac disease is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors
- Celiac disease has a strong genetic component. Those with a family history of celiac disease (or other autoimmune conditions) are more likely to develop it.
- Certain genes, especially HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, are tightly linked to the disease. But having those genes doesn’t mean someone will get celiac disease.
Immune System Response
- Celiac disease takes place when the body misinterprets gluten as something harmful to the body. This causes an immune response that injures the lining of the small intestine, resulting in trouble absorbing nutrients.
- The immune system attack on the intestines can lead to inflammation and eventually more damage over time.
Environmental Triggers
- Environmental triggers, including infections or stressful life events, can play a role in starting celiac disease, particularly in a genetically susceptible individual.
- The onset of the disease can be triggered through exposure to gluten during infancy, especially when combined with other factors.
Celiac Disease Symptoms
The celiac disease is not the same as a food allergy, so the symptoms are also different. If you are allergic to wheat but eat something containing wheat, you may experience itchy or watery eyes or difficulty breathing.
Celiac disease symptoms in adults
If you have celiac disease and accidentally consume gluten, you may have symptoms like:
- Abdominal pain
- Anaemia
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness
- Bone or joint pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Gas
- Heartburn
- Itchy, blistery rash (doctors call this dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Headaches or fatigue
- Mouth ulcers
- Nausea
- Nervous system injury, including numb or tingling hands or feet, balance problems, or changes in awareness
- Weight loss
Celiac disease symptoms in children
Celiac disease increases the chances of digestive issues in children.
- Bloating or belly swelling
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Pale, foul-smelling poop
- Upset stomach or vomiting
- Weight loss
Common Symptoms of Celiac Disease in Females:
- Digestive Issues
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Skin Conditions
- Weight Loss or Unexplained Weight Gain
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Bone and Joint Pain
- Neurological Symptoms
Early diagnosis and management of celiac disease are important to reduce these symptoms and improve the quality of life. If you experience these symptoms, consulting a celiac disease specialist is essential for proper testing and treatment.
Risk Factors of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease tends to be more common in people who have:
- A family member with celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis
- Diabetes type 1
- Turner syndrome or Down syndrome
- Thyroidautoimmune disease
- Microscopic colitis (lymphocytic or collagenous colitis)
- Addison's syndrome
Celiac Disease Complications
Untreated, celiac disease can cause:
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition develops when your small intestine is unable to absorb adequate nutrients. Anaemia and weight loss can result from malnutrition. It can induce poor development and short stature in children.
- Bone weakening: Deficiency of calcium and vitamin Dcan cause bone softening (osteomalacia or rickets) in children and bone density loss (osteopenia or osteoporosis) in adults.
- Infertility and miscarriage: Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D might contribute to infertility and miscarriage.
- Lactose intolerance: Damage to the small intestine can cause stomach discomfort and diarrhea after eating or drinking lactose-containing dairy products. You may be able to accept dairy products again once the intestine has recovered.
- Nervous system problems: Some celiac disease patients may experience seizures or nerve disorders in their hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy).
- Cancer: People with celiac disease who do not follow a gluten-free diet are more likely to develop cancer, including intestinal lymphoma and small intestine cancer.
Celiac Disease Diagnosis
A physical examination and a medical history are used to make a diagnosis. Doctors will also perform various tests to assist confirm a diagnosis. Antiendomysium (EMA) and anti-tissue transglutaminase (TGA) antibodies are frequently elevated in celiac disease patients. Celiac disease blood tests can detect these conditions. They are the most reliable when tests are conducted when gluten is still present in the diet.
Common celiac disease blood test include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Liver function tests
- Cholesterol test
- Alkaline phosphatase level test,
- Serum albumin test.
A skin biopsy can help doctors detect celiac disease in persons with dermatitis. The doctor will extract microscopic bits of skin tissue for examination under a microscope during a skin biopsy. If the skin biopsy results and blood tests suggest celiac disease, an internal biopsy may not be required.
When Celiac disease tests or skin biopsies are inconclusive, an upper endoscopy can be used to diagnose celiac disease. During an upper endoscopy, a narrow tube called an endoscope is put through the mouth and down into the small intestines. The doctor can inspect the intestines and check for villi damage using a tiny camera linked to the endoscope. In addition, the doctor can do an intestinal biopsy, which includes removing a tissue sample from the intestines for analysis.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentCeliac Disease Treatments
The only way to treat celiac disease is to eliminate gluten from the diet. This permits the intestinal villi to recover and begin correctly absorbing nutrients. The doctor will instruct patients on how to eliminate gluten while eating a good and healthy diet. They will also educate you on how to read food and product labels so you can detect any gluten-containing ingredients.
When gluten is removed from the diet, symptoms might improve within days. However, patients should not stop consuming gluten until they have been diagnosed. Premature gluten removal may interfere with test findings and result in an incorrect diagnosis.
Celiac Disease Medications
There are no specific medications to cure celiac disease. However, medications may be used to manage symptoms, such as corticosteroids for inflammation or other drugs to manage related conditions like osteoporosis or anemia.
Celiac Disease Diet
The cornerstone of treatment is a strict gluten-free diet. Avoiding gluten, found in wheat, barley, and rye, helps heal the intestine and prevents symptoms. This is the most effective way to manage celiac disease.
Celiac Disease Antibodies
Blood tests are used to measure celiac disease antibodies, such as tTG-IgA, to diagnose and monitor the disease. High levels of these antibodies indicate an immune response to gluten.
Foods to Avoid in Celiac Disease
Individuals with celiac disease should avoid foods containing gluten, such as bread, pasta, baked goods, and certain processed foods that may contain hidden gluten.
Vitamins for Celiac Disease
Since celiac disease can affect nutrient absorption, supplements like iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins may be prescribed to address deficiencies.
When to See a Doctor for Celiac Disease?
If you suspect you have celiac disease or experience symptoms, it's important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are some signs that indicate you should seek medical attention:
- Persistent Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Unexplained Fatigue:
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Nutrient Deficiencies
- Family History
- Skin Rash
Frequently Asked Questions
How does celiac disease start?
Celiac disease begins when someone who is genetically prone to it eats foods containing gluten (found in wheat, barley, and rye). Over time, the immune system reacts to gluten and harms the small intestine.
Is celiac disease very serious?
Yes, celiac disease is a serious autoimmune condition. If left untreated, it can lead to various health issues like nutrient deficiencies and small intestine damage. But by avoiding gluten in your diet, you can usually manage it well.
Who gets celiac disease?
Celiac disease can affect anyone, young or old. It often runs in families, so if someone in your family has it, you might be more at risk. It can start at any age.
Is celiac disease serious?
Yes, celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disorder. Untreated it can lead to long-term health issues including malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and a higher risk of certain cancers. But, if you do follow a strict gluten-free regimen, you are able to control the symptoms and prevent complications.
Who gets celiac disease?
Celiac disease can occur in anyone, but it is more common for those with a family history of the disorder or other autoimmune conditions. It can progress at any stage in life, including adult onset, and is most prevalent among those of European descent. Genetic testing can show who is at greater risk.
What foods trigger celiac disease symptoms?
Gluten is a protein in certain foods, including wheat, barley and rye, that causes symptoms in people with celiac disease. What foods are common to avoid: bread, pasta, baked goods, and some processed foods. Cross-contamination with gluten is another concern, so reading labels thoroughly is crucial.
