Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic, long-lasting health condition that affects how the body turns food into energy and causes high blood glucose levels.
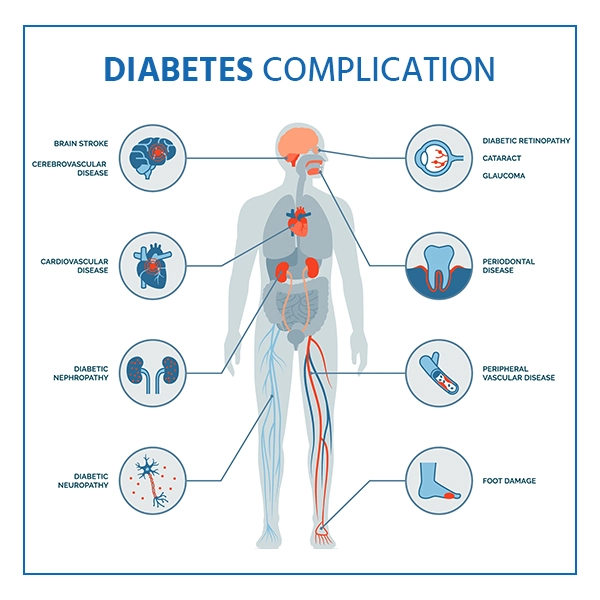
This occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not use the insulin produced as effectively as it should. Excessive blood sugar remains in the bloodstream when there is insufficient insulin or when cells stop responding to insulin and can lead to serious health issues such as vision loss, heart disease, and kidney disease over time.
Taking diabetes medication as needed, receiving diabetes self-management education and support, and keeping health care appointments can help to lessen the impact of diabetes on your life.
Types of Diabetes
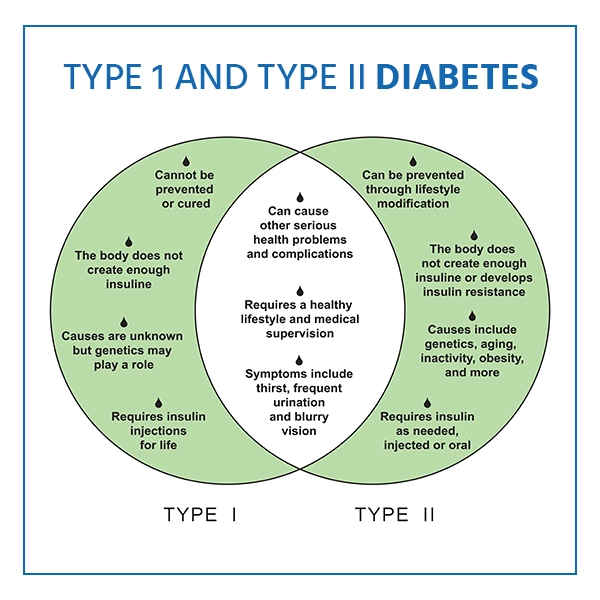
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant).
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body accidentally attacks itself) that restricts the body from producing insulin. Type 1 diabetes affects approximately 5-10% of all diabetics. Type 1 diabetes symptoms frequently appear quickly. This is commonly diagnosed in children, teenagers, and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: With type 2 diabetes, the body does not use insulin well and cannot maintain normal blood sugar levels. It takes years to develop and is usually diagnosed in adults. Because the symptoms are not noticeable, it is critical to have blood sugar tested. Type 2 diabetes can be avoided or delayed by adopting healthy lifestyle changes such as losing weight, eating nutritious foods, and exercising regularly.
- Gestational Diabetes: Pregnant women who have never had diabetes can develop gestational diabetes. The baby may be at greater risk of health problems if the mother has gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually clears up after the baby is born, but it increases the risk of later developing type 2 diabetes. The baby has a higher chance of becoming obese as a child or adolescent with type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Prediabetes: This is the stage preceding Type 2 diabetes. In prediabetes, the blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as having Type 2 diabetes.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
Symptoms of Diabetes
If you experience any of the following diabetes symptoms, consult your doctor about having your blood sugar tested:
- Blurred vision
- Increased thirst
- Numbness in the hands or feet
- Weak, tired feeling
- Unplanned weight loss
- Dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Frequent unexplained infections
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes patients may also experience nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can manifest in a matter of weeks or months and can be severe. Type 1 diabetes typically begins in childhood, adolescence, or young adulthood, however it can occur at any age.
- Genetics: A family history of certain medical disorders might raise the chance of developing cataracts.
- Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes symptoms can take years to appear. Some people experience no symptoms at all. Type 2 diabetes most commonly affects adults, but it is becoming more common in children and teenagers. Because symptoms can be difficult to detect, it is critical to understand the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. If you face any of these diabetes symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor.
- Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) is usually asymptomatic. Between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, the pregnant woman should be tested for gestational diabetes. Medication changes can be made to protect your health and the health of your baby if necessary.
When to see a doctor?
If a person has high blood sugar levels or symptoms of high blood sugar, such as excessive urination (peeing), he or she should see a doctor. If the symptoms are severe, the doctor may refer the patient to a specialist, such as an endocrinologist or a diabetes expert.
Get the best diabetes treatment from our Diabetologists at Medicover Hospitals
Causes
Diabetes, regardless of type, is caused by having too much glucose circulating in the bloodstream. However, the cause of your high blood glucose levels varies depending on the type of diabetes.
- Causes of Type 1 diabetes: This is a disease of the immune system. Insulin-producing cells in the pancreas are attacked and destroyed by the body. Glucose accumulates in the bloodstream if insulin is not present to allow glucose into the cells. A virus can also cause an immune system attack.
- Cause of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes: The cells in the body do not allow insulin to work as it should to allow glucose into the cells. Insulin resistance has developed in the body's cells. The pancreas seems unable to keep up and produce sufficient insulin to overcome this resistance. Glucose levels in the bloodstream rise.
- Cause of Gestational Diabetes: During pregnancy, hormones produced by the placenta make the body's cells more resistant to insulin. The pancreas cannot to produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance. There can be an excess of glucose in the bloodstream.
Risk Factors
- Type 1 Diabetes: An immune response can be the cause of type 1 diabetes (the body attacks itself by mistake). The risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as they are for type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Risk factors include
- Family history Having a type 1 diabetes to parent, brother, or sister.
- Age Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, but it is most common in children, teenagers, and young adults
- Type 2 Diabetes: An individual is at risk for type 2 diabetes if they:
- Are overweight
- Have prediabetes
- Have a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes
- Are 45 years or older
- Have ever had gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy)
- Are physically active less
- Have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Proven lifestyle changes can help to avoid or delay type 2 diabetes. These include losing weight if you are overweight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
- Gestational Diabetes: A person is at risk for gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant) if they:
- Are overweight
- Had gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy
- Are more than 25 years old
- Have a hormone disorder, like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Have a family history of type 2 diabetes
Dos and Don’ts
Healthy eating is the keystone of diabetes treatment. A diabetic can often manage the condition through diet and exercise. When a diabetic patient ignores this critical aspect of diabetes management, his or her blood sugars become uncontrolled.
When you have diabetes, sticking to a set of diet "Do's" and "Don'ts" makes it easier to manage your blood sugar levels. Follow the dietary guidelines below to manage your diabetes and blood sugar levels.
Diabetes is a serious medical condition and controlling blood sugar levels with a healthy diet is an essential part of managing it. Always follow your doctor's or registered dietitian's dietary recommendations, and consult with them if you're unsure about what's best for you.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Diabetes Care at Medicover Hospitals
Medicover’s team of Diabetes Experts, Dieticians, Endocrinologists, Exercise Management Consultants, Counselors and Diabetes Educators provide an effective way to manage the condition and prevent and treat the complications. Our Diabetes Specialists also help with lifestyle changes and in coping with the emotional challenges that this chronic condition brings. Stay connected to our holistic diabetes care at all times with a unique blend of medical and emotional care.