The symptoms of gingivitis are
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Sore gums
- Red gums
- Halitosis or Bad Breath
- Gum recession
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- Pain while chewing foods.
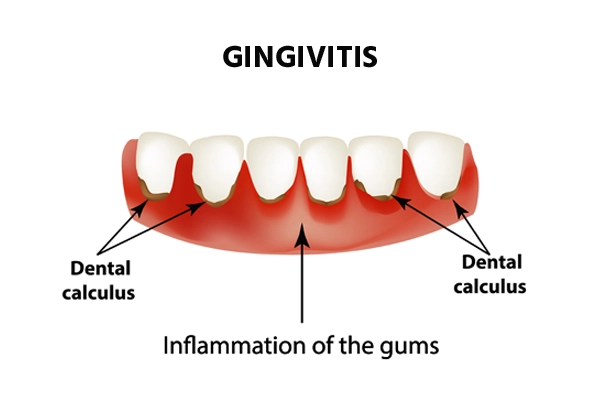
Gingivitis is a common non-destructive gingival disease. It causes inflammation of the gums and is considered a mild form of gum disease (periodontal disease).
It's important to take gingivitis seriously or else it can cause serious dental problems like periodontitis and loss of all the teeth. It is possible to cure or reverse it with timely dental treatment.
Gum diseases are divided into two different types
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionThe symptoms of gingivitis are

Follow your regular dental checkups. If you detect any gingivitis symptoms, make a dental appointment with a dentist as soon as possible. As this gum disease can be cured or reversed, it is crucial that its symptoms are not ignored and its progression to periodontitis is stopped with timely dental treatment.
Get the best treatment for gingivitis from our dentists at Medicover Hospitals.
Gingivitis occurs when plaque and bacteria accumulate on teeth and gums, leading to inflammation. Key causes include:
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup. Several factors can increase the risk of developing gingivitis, including:
Gingivitis progresses through distinct stages if left untreated:
Early treatment and proper oral hygiene can prevent gingivitis from advancing to severe stages. Regular dental cleanings and checkups are essential.
It is possible to prevent gingivitis by practising good oral health care habits and getting regular dental check-ups. Follow the below-given oral hygiene tips to stay away from dental problems.
The following steps are used to diagnose gingivitis:
If you can catch it early, gingivitis can be treated and prevented from developing into more serious, damaging gum diseases like periodontitis. Watch for signs of gum disease. Dental visits help!
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentEarly dental treatment reverses symptoms of gingival disease and prevents its progression to dental periodontitis. It includes
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. Its symptoms include gum swelling pain, and easy bruising during tooth brushing. Ignoring its symptoms can lead to periodontitis and also affect the overall health of the person. Its treatment includes dental cleaning involving scaling and root planning and maintaining good oral hygiene.
|
Do’s |
Don’ts |
|
Maintain good oral health |
Smoke and chew tobacco products. |
|
Stick to proper tooth brushing techniques. |
Compromise with brushing your teeth regularly |
|
Use fluoride toothpaste |
Take much sugary foods and soda beverages. |
|
Regular dental check-ups |
Ignore the treatment if you are diabetic |
|
Replace your toothbrush every 2-3 months. |
Eat too hot or too cold food items. |
Follow the do’s and don'ts for gingivitis to prevent gingival diseases and other serious dental issues. Gingivitis is a reversible condition, so treating it on time can prevent serious dental problems.
People at higher risk of gingivitis include those with poor oral hygiene, smokers, pregnant women, people with diabetes, and those with certain medications or hormonal changes.
To prevent gingivitis, practice good oral hygiene: brush teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, use an antimicrobial mouthwash, and visit the dentist regularly for cleanings.
To reduce bad breath from gingivitis, maintain proper oral hygiene, brush your tongue, use mouthwash, stay hydrated, and visit your dentist for regular cleanings.
Yes, gingivitis is reversible with proper dental care, such as regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings. Early treatment can restore gum health and prevent further complications.
Gingivitis causes red, swollen gums that bleed easily but does not affect bone or teeth stability. Periodontitis involves gum recession, bone loss, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath.
The progression from gingivitis to periodontitis varies depending on factors like oral hygiene, smoking, and medical conditions. It can take a few months to years without proper care.
If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to:Periodontitis (severe gum disease), Gum recession, Tooth loss, Increased risk of systemic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
Click here to request a callback!