Gout
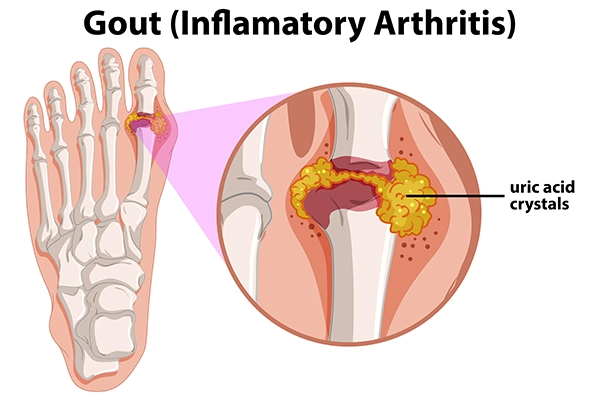
Gout is a complicated kind of arthritis that causes sudden, acute pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints, most commonly the big toe.
Gout attacks can strike without warning, waking up in the middle of the night with the big toe in pain and having a burning sensation. Even the weight of the bedsheet on the affected joint may feel uncomfortable because it becomes swollen, and sensitive.
Gout symptoms
Gout symptoms and indicators nearly typically strike unexpectedly, and frequently at night. They are as follows:
- Joint discomfort: Gout is most commonly associated with the big toe, but it can affect any joint. Ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers are among the other joints that are typically afflicted. The pain will most likely be the worst during the first four to twelve hours after it starts.
- Discomfort that is continuous: Some joint discomfort may remain from a few days to a few weeks after the most acute pain has subsided. Attacks in the future are more likely to continue longer and damage more joints.
- Inflammation and redness: Swollen, sensitive, heated, and redness develop in the afflicted joint or joints.
- Restricted range of motion: Restricted range of motion You may not be able to move your joints normally as gout worsens
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
When to see a doctor?
Visit a doctor if you get sudden, severe pain in a joint. Untreated gout can lead to increased discomfort and joint damage. If you have a fever and a heated and inflamed joint, this could be an indication of infection. Seek medical help right once. Get the best treatment for Gout at Medicover Hospitals from the top orthopedists
Causes of Gout
Gout occurs when urate crystals build up in your joints, producing inflammation and excruciating pain. When your blood contains too much uric acid, urea crystals can form. When your body breaks down purines, which are chemicals found naturally in your body, uric acid is produced.
Purines can also be found in some foods, such as red meat and organ meats like liver. Anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout, and tuna are examples of purine-rich seafood. Higher amounts of uric acid are promoted by alcoholic beverages, particularly beer, and drinks sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose).
Uric acid dissolves in your blood and flows through your kidneys into your urine in normal circumstances. However, your body may create too much uric acid or your kidneys may remove too little uric acid at times. Uric acid can build up in joint or surrounding tissue, generating sharp, needlelike urate crystals that cause pain, inflammation, and swelling.
Gout Risk factors
There are many factors that can add-up to the symptoms of gout and worsen it further.
- Diet: Consuming a diet high in red meat and seafood, as well as beverages sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose), raises uric acid levels, putting you at risk for gout. Gout is also exacerbated by alcohol consumption, particularly beer.
- Weight: Your body produces more uric acid when you're overweight, and your kidneys have a harder time clearing it.
- Medical problems: Gout is caused by a number of diseases and situations. Untreated high blood pressure and chronic illnesses like diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and heart and kidney disease are among them
- Medications: Low-dose aspirin and various hypertension drugs, such as thiazide diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and beta-blockers, might raise uric acid levels. Anti-rejection drugs can also help.
- Gout runs in the family: You're more likely to acquire gout if other members of your family have had it.
- Age and gender: Gout is more common in men than in women, owing to women's lower uric acid levels. Women's uric acid levels, on the other hand, approach those of males after menopause. Men are also more prone than women to acquire gout symptoms earlier in life, usually between the ages of 30 and 50, whereas women often develop symptoms after menopause.
- Recent surgery or a traumatic event: A gout episode can occasionally be triggered by recent surgery or trauma. Getting vaccinated can cause gout flare-ups in certain people.

Complications
- Gout that flares up again and again: Some people may never have to deal with gout symptoms again. Others may get gout on multiple occasions throughout the year. In those with recurrent gout, medications may help prevent episodes. Gout, if left untreated, can cause joint erosion and damage.
- Untreated Gout: Gout can lead to the formation of tophi, which are urate crystal deposits under the skin. Tophi can appear anywhere on your body, including your fingers, hands, feet, elbows, and the Achilles tendons in the backs of your ankles. Tophi are normally painless, although they can swell and become sensitive during gout bouts.
- Stones in the kidneys: Gout patients' urinary tracts can get clogged with uric acid crystals, resulting in kidney stones. Kidney stones can be prevented with the use of certain medications.
Diagnosis of Gout
Gout drugs are divided into two categories, each of which addresses a different issue. The first type helps to alleviate the pain and inflammation associated with gout attacks. The second type reduces the quantity of uric acid in your blood, which helps to prevent gout problems.
The frequency and intensity of your symptoms, as well as any other health issues you may have, will determine which drug is best for you.
- Test for joint fluid: A needle may be used by your doctor to drain fluid from your damaged joint. When the fluid is viewed under a microscope, urea crystals may be visible
- A blood test is required: A blood test to determine the amounts of uric acid in your blood may be recommended by your doctor. However, blood test results can be deceiving. Some people have high levels of uric acid but never get gout. And other people have gout symptoms but no abnormally high levels of uric acid in their blood.
- X-ray: This test uses X-rays of the joints can help rule out alternative causes of joint inflammation.
- Ultrasound: This technique detects urate crystals in joints or tophi using sound waves
Computerized tomography with dual energies (DECT). To visualize urate crystals in joints, this test combines X-ray pictures acquired from a variety of angles.
Computerized tomography with dual energies (DECT). To visualize urate crystals in joints, this test combines X-ray pictures acquired from a variety of angles.
Treatment of Gout
Gout drugs are divided into two categories, each of which addresses a different issue. The first type helps to alleviate the pain and inflammation associated with gout attacks. The second type reduces the quantity of uric acid in your blood, which helps to prevent gout problems.
The frequency and intensity of your symptoms, as well as any other health issues you may have, will determine which drug is best for you.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Gout Dos and Don’ts
A person with gout has to follow sets of do’s and don’ts to manage gout and related symptoms.
A person with gout has to follow sets of do’s and don’ts to manage gout and related symptoms.
Gout Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover Hospitals, we have the most trusted team of doctors and medical experts who are experienced in providing excellent healthcare services to patients with compassion and care. Our diagnostic department is equipped with modern technology and equipment to conduct the tests required for the diagnosis of Gout based on which a dedicated treatment plan is designed. We have an excellent team of specialists, rheumatologists, and orthopedists who diagnose and treat this condition with utmost precision that brings successful treatment outcomes. The entire treatment process and the post-treatment follow-up schedules are designed adequately to ensure lasting and long-term recovery of the patients.