Understanding Anemia
Anaemia is a condition that indicates a decrease in healthy red blood cells (RBCs) or a reduced amount of haemoglobin (Hb) within them. Haemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body while returning carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation.
Role of iron in the body:
- Iron is essential for the production of haemoglobin.
- It is required for the proper function of the immune system
- It is necessary for maintaining healthy cells, hair, skin, and nails.
- Iron helps in a healthy pregnancy, increases energy, and improves athletic performance.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
What is Iron Deficiency Anaemia?
Iron deficiency anaemia (IDA) is a specific type of anaemia that develops when the body does not have sufficient iron to produce red blood cells.
It is a type of common nutritional deficiency disease.
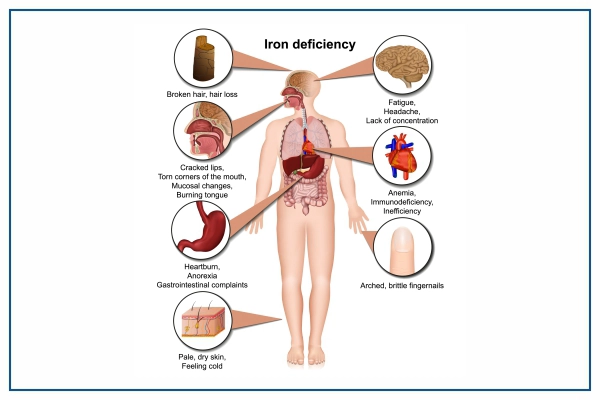
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anemia
The symptoms vary among individuals. Initially, they can be mild, but after a prolonged period, as the deficiency worsens, the signs and symptoms become evident.
When to see a doctor?
Untreated anaemia can lead to serious health issues. If you suspect or experience the signs and symptoms, it is mandatory to see a doctor. Consult our general physicians and haematologists for more information and adequate treatment for anaemia.
What Causes of Iron Deficiency Anemia?
The causes of Iron-deficiency anaemia are as follows:
- Low iron diet: Without sufficient iron-rich foods, there's a risk of developing IDA.
- Changes in the body: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, and adolescents experiencing growth spurts, require more iron for red blood cell production.
- Gastrointestinal tract problems: Certain gastrointestinal conditions hinder iron absorption, leading to IDA despite adequate dietary iron intake.
- Loss of blood: Rapid loss of blood from surgery, trauma, or childbirth, as well as chronic blood loss from conditions like hemorrhoids, gastrointestinal disorders, or heavy menstrual bleeding, can cause IDA. Regular use of certain medications like aspirin and ibuprofen can also contribute.
Risk Factors of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Individuals with the following health issues are at increased risk for iron deficiency anaemia:
The other groups at risk are:
- Infants with low birth weight and premature birth lack sufficient iron
- Young children who fail to get adequate iron from iron-rich foods or iron supplements are more prone to developing nutritional anaemia.
- Pregnant women may get iron deficiency anaemia due to increased blood volume, which is necessary for baby growth.
- Women with heavy periods lose more blood, leading to low iron levels in the body.
- Blood donors lack iron due to frequent blood donations.
- Vegetarians often suffer from iron deficiency as a result of dietary restrictions.
Complications of Iron Deficiency Anemia
The iron deficiency anaemia complications include:
How is Iron Deficiency Anemia diagnosed?
Iron deficiency anaemia diagnosis is made by blood tests, including a complete blood count (CBC). The doctor may recommend more tests to evaluate iron levels, serum ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, and transferring. Iron deficiency tests usually show the following results:
- Low haemoglobin (Hg) and hematocrit (Hct)
- Low mean cellular volume (MCV)
- Low serum iron (FE)
- Low ferritin
- Low iron saturation
- High transferrin or total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
A peripheral blood smear test may show small, microcytic and hypochromic red blood cells in chronic iron deficiency anaemia. The white blood cell count (WBCs) may be low, and the platelet count may be high or low.
Additional iron deficiency tests include:
- Upper and lower endoscopy
- Faecal occult blood test
- Gynecologic evaluation in women
- Test for hematuria or hemoglobinuria
Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Treatment varies from person to person based on the severity and causes of Anemia.
Blood loss from a gastrointestinal problem:
In the case of an ulcer, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics or other medications to treat the condition. The bleeding caused by a cancerous tumour or a polyp will need surgery to remove it.
Blood loss from heavy menstrual periods:
In case of mild anaemia due to iron malabsorption or lower iron levels, the doctor may recommend:
- In case of mild anaemia due to iron malabsorption or lower iron levels, the doctor may recommend.
- Iron tablets to build up iron levels as quickly as possible. Iron supplements are available in the form of tablets, capsules, chewable tablets, and liquids. Take iron pills only as per your doctor's prescription.
Eat iron-rich foods such as:
- Meat
- Fish
- Eggs
- Beans
- Dried fruits
- Dark green, leafy vegetables
- Peas
- Fortified foods
Also, foods rich in vitamin C:
- Oranges
- Broccoli
- Tomatoes
- Strawberries
- Kiwis
- Blackcurrants
In serious cases, including shortness of breath and chest pain, the doctor may suggest red blood cell transfusions. Usually uncommon, blood transfusions are preferred for cases with severe iron deficiencies only.
Dos and Don’ts
Follow the below mentioned Do’s and Don’ts to prevent iron deficiency disease and its complications.
Iron Deficiency Anaemia Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, our expert general physicians and hematologists, delivers exceptional care for iron deficiency anemia. We offer complete healthcare services and use a diverse approach for successful treatment. We ensure exceptional treatment outcomes through providing world-class facilities at an affordable pricing.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Frequently Asked Questions
Anaemia is a medical condition characterized by a decreased number of red blood cells or a low
concentration of haemoglobin in the blood, leading to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity and potential
health problems.
Anaemia can be caused by various factors, including nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, folate),
chronic diseases (kidney disease, cancer), bone marrow disorders, genetic conditions (thalassemia,
sickle cell anaemia), and certain medications.
Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, headache, cold
hands and feet, chest pain, and irregular heartbeats. However, symptoms can vary depending on the
severity and underlying cause of anaemia.
Iron-rich foods like spinach, beans, fortified cereals, and lean meats can be consumed naturally. Pair
them with vitamin C sources for better absorption. Coffee, tea, and calcium-rich foods that hinder iron
absorption should also be avoided.
Iron deficiency anaemia in pregnancy occurs when a pregnant woman lacks enough iron to produce adequate
haemoglobin for herself and her baby. It can cause fatigue, weakness, and other complications,
emphasizing the importance of proper management through iron supplementation and dietary adjustments.