What is Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is an autoimmune condition that causes signal transmission issues at the neuromuscular junction. As a result, the muscles get tired fast and improve after rest.
It affects the muscles that regulate the below-listed actions in the early stages;
- Eye movements
- Facial expressions
- Chewing
- Swallowing
As the condition worsens, the neck and limb muscles may be affected, making it difficult to hold the head up, walk upstairs, and raise the arms. Breathlessness may occur if left untreated.
Although this condition does not run in families, those who develop autoimmune conditions are more likely to develop myasthenia gravis.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
What are the Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis (MG)?
Generalized weakness usually develops within two years of illness. In general, MG symptoms include:
Severe myasthenia gravis can lead to respiratory muscle weakness. It is a medical emergency and requires ventilator support.
Approximately 15% to 20% of MG patients may experience at least one crisis triggered by factors like:
- Infection
- Stress
- Surgery
- Medication reactions
For emergency myasthenia gravis care, please book an appointment with our specialists.
What are the Primary Causes of Myasthenia Gravis?
The two primary causes of Myasthenia Gravis include;
Autoimmune Response
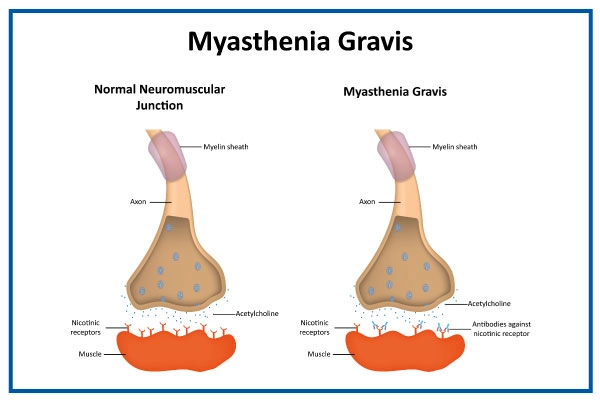
Myasthenia gravis is primarily an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the body's tissues. The immune system releases antibodies that target and block acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscles, and blocking these receptors disrupts muscle function.
Thymus Involvement
The thymus gland, part of the immune system, plays a role in developing myasthenia gravis. Sometimes, the thymus gland is abnormally large or contains tumors that trigger or exacerbate the autoimmune response.
Surgical removal of the thymus (thymectomy) is a standard treatment for myasthenia gravis in cases involving the gland.
What are the Common Causes of Myasthenia Gravis
- Here are a few common causes of MG;
- Smoking and tobacco chewing
- Physical inactivity
- Fatigue
- Obesity
- Insufficient diet
- A lower rate of fish consumption
What are the Risk Factors of Myasthenia Gravis?
Here are some factors that contribute to the development of MG:
- Genetic factors: Myasthenia Gravis is not directly inherited. Some people may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to developing the condition.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors or infections may trigger the onset of myasthenia gravis in individuals genetically predisposed to the condition. However, specific triggers have not been definitively identified.
- Pregnancy: Children born to mothers with Myasthenia Gravis rarely have a chance of developing it. If treated immediately, they recover in two months.
What are Tests Conducted to Diagnose Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis can be diagnosed based on the symptoms and certain tests. The doctor will inquire about the medical history and symptoms throughout the physical examination.
Edrophonium Test
The doctor will inject edrophonium chloride to see if it improves muscle strength. If it happens, it might be an indication of myasthenia gravis.
Ice pack Test
If you have a drooping eyelid, the doctor may place an ice pack on it for two minutes to examine if the cold sensation affects it.
Blood Test
Routine blood tests to rule out other causes. Achr and musk autoantibodies are to be tested.
Repetitive Nerve Stimulation
This test sends small electrical pulses through electrodes into the muscles to examine if your nerves respond to the impulses.
Imaging Test
The doctor may recommend a CT scan or an MRI to look for a tumour in the thymus area.
Pulmonary Functioning Tests
In the pulmonary functioning test, the doctor will examine the breathing ability to check if it has affected the lungs.
What are the Options Available for Myasthenia Gravis Treatment?
MG is a treatable condition; many patients may live normal lives after treatment. Here are the four different options for treating Myasthenia Gravis.
- Medicines : Anticholinesterase medications, steroids, or medications that may be used to suppress the immune system's reaction (immunosuppressive).
- Thymectomy : The thymus gland is surgically removed in all patients with myasthenia who has hyperplasia or neoplasm of thymus.
- Plasmapheresis : A technique in which abnormal antibodies are removed from the blood and replaced with normal antibodies from donor blood.
- Immunoglobulin : It is a blood product that helps to reduce the immune system's attack on the neurological system. It is administered intravenously (IV).Both are useful in patients who are in myasthenia crisis
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, individuals with myasthenia gravis can lead fulfilling lives with the condition. While there is no known cure, effective treatment and symptom management can significantly improve their quality of life.
Myasthenia gravis is not directly caused by stress. It can exacerbate its symptoms. One can control this condition effectively by managing stress and ensuring adequate rest.
Unfortunately, myasthenia gravis currently has no known cure. Nevertheless, several treatment options are available to manage the condition effectively. Refer to our page for details!
Myasthenia gravis is not typically preventable as it is primarily an autoimmune disorder with genetic factors. It can develop in individuals with a genetic predisposition.