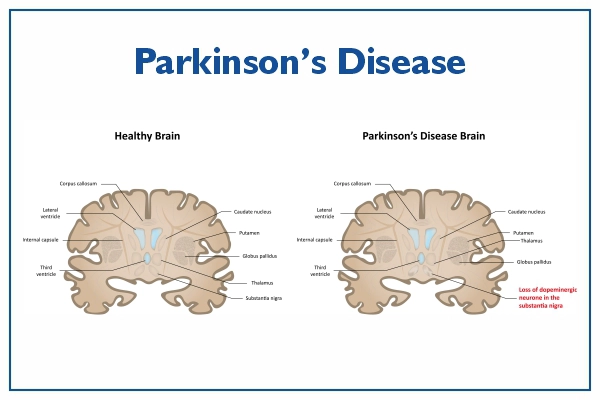
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson's disease is a long-term brain disorder impacting nerve cells, affecting movement and various aspects of life. Though its cause remains unknown, treatments like medication and surgery can help manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. While not typically fatal, it can lead to severe complications.
Types Of Parkinson's Disease
The types of Parkinson's disease are as follows:
- Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease
- Vascular Parkinsonism
- Drug-induced parkinsonism
- Early-Onset Parkinson's
- Multiple system atrophy
- Progressive supranuclear palsy
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Normal-pressure hydrocephalus
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
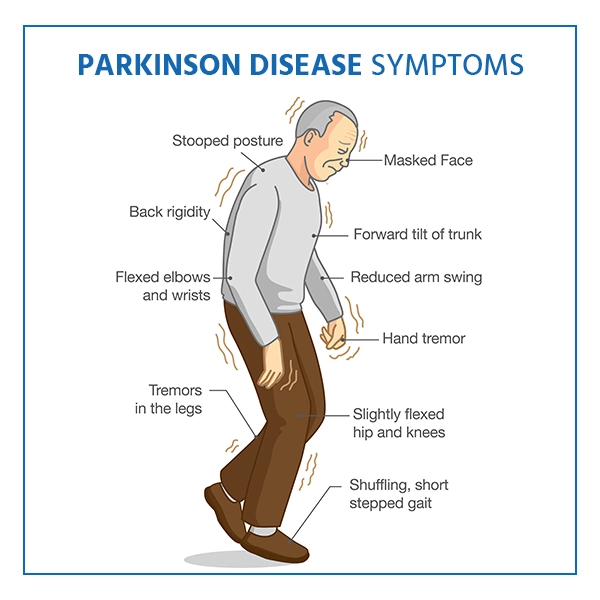
What are the Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson's disease symptoms appear slowly. They usually begin with a tremor in one hand and a sensation of rigidity throughout the body. Other symptoms emerge over time, and some people develop dementia.
The following are some early indications of Parkinson's disease:
- Tremors
- Bradykinesia
- Rigidity
- Postural instability
- Freezing
- Micrographia
- Masked face
- Speech changes
- Stooped posture
Other common symptoms include:
When to see a doctor?
Feeling shaky, tense, or unsteady? See a doctor. If it seems like Parkinson's, they may refer you to a neurologist. Get top-notch Parkinson's treatment at Medicover Hospitals with our expert neurologists.
What are the Causes and Risks Factors of Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson's is a neurological disorder with unclear causes. Genetics and environment likely play a role. Variants in genes like alpha-synuclein may contribute. Certain toxins, like MPTP, can trigger symptoms in susceptible individuals. Around 10 million are affected annually.
What are the Risk Factors of Parkinson’s Disease?
The risk factors are as follows:
- Age: Risk increases with age, with most cases diagnosed after the age of 60.
- Genetics: A family history of Parkinson's disease can increase the risk.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop Parkinson's disease than women.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins or environmental factors may increase the risk.
- Head trauma: Traumatic brain injuries may be associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease.
- Certain medications: Some drugs have been linked to a higher risk of Parkinson's disease.
- Rural living: Studies suggest that people living in rural areas may have a slightly higher risk.
What are the Complications of Parkinson’s Disease?
The consequences of Parkinson's disease on mobility are arguably the most well-known. Rigid muscles, delayed movements and shaking are the most obvious signs. The following are some well-known complications:
- Cognitive Problems:
- Depression and Anxiety:
- Difficulty in Swallowing:
- Dementia:
- Impaired sense of smell:
What are the Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease?
Diagnosis is challenging at any stage of the disease, especially during the initial stages. A diagnosis cannot be made with a specific test. Physical and neurological exams will most likely be performed periodically to measure changes in reflexes, coordination, muscular strength, and mental function. Doctors use clinical factors to diagnose the condition.
Useful diagnostic tools include:
- Blood tests
Although blood tests cannot diagnose Parkinson's disease, they can assist the doctor in identifying alternative causes of parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy or corticobasal degeneration.
- Genetic testing
If they have a family history of parkinsonism, genetic testing may help the doctor identify the main reason.
- DaTscan
A DaTscan is a type of imaging that allows a doctor to examine how much dopamine is present in the brain. If the scan reveals an abnormally low level, the doctor's Parkinson's diagnosis may be confirmed.
- Magnetic resonance imagining (MRI)
A brain tumour, normal pressure hydrocephalus, or vascular parkinsonism can all be detected using an MRI
What are the Medications for Parkinson's Disease?
Parkinson's disease is treated with various medications.
Parkinson's disease is treated with various medications.
- Carbidopa and levodopa are tremor-controlling drugs used in combination with other drugs to reduce the tremors.
- Benzodiazepines, sometimes known as tranquillisers, can temporarily relieve tremors.
- Beta-blockers might also be used to ease out some symptoms of the disease like high blood pressure.
- Anti-seizure drugs like primidone can help those with tremors which aren't responding to beta-blockers.
- Most tremors can be treated with botulinum toxin, often known as Botox.
Lifestyle Changes And Self-Care for Parkinson's Disease
Making lifestyle changes may help people with Parkinson's disease.
- Healthy diet:Constipation is a common symptom of Parkinson's disease, so eating a high-fibre diet of fruits, vegetables, and grains, as well as drinking enough water, might help avoid it.
- Exercise:Exercise can improve physical strength and balance while reducing sadness and anxiety.
- Work:Simple workplace adjustments, flexible hours, and regular medication assessment and adjustment may be required to continue working safely and effectively
- Relationships and sex:Sexual desire, performance, or pleasure may be reduced in patients with Parkinson's disease. Others may experience a preoccupation with sexual ideas due to dopamine substitution medications. If this is happening, individuals should seek medical advice.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Frequently Asked Questions
No, Parkinson's disease can affect people of any age, although it is more common in older adults.
Common symptoms include tremors, stiffness, slow movement, and impaired balance. However, symptoms can vary greatly among individuals.
Diagnosis is usually based on medical history, a neurological examination, and sometimes imaging tests like MRI or CT scans.
Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson's disease, but various treatments, including medications and therapies, can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate rest, and stress management techniques can all help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining a regular bowel routine can help remove waste matter effectively, which is important for managing symptoms.