Urinary tract infection
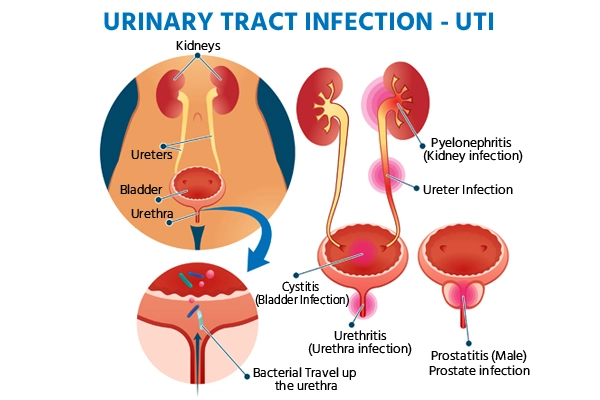
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are common urine infections that can occur anywhere in the urinary tract (which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra).
When the UTI happens in the lower urinary tract, it is known as a bladder infection ( cystitis), and when it involves the upper urinary tract, it is called a kidney infection (pyelonephritis).
Women are more likely than men to have a urinary tract infection. If a UTI spreads to the kidneys, it might give rise to serious health problems.
Symptoms of Urinary tract infection
Symptoms of a lower urinary tract or bladder infection include:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Despite having an empty bladder, there is an urge to urinate.
- In the groin or lower abdomen, there is pressure or cramping.
Symptoms of an upper urinary tract or kidney infection include:
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lower back pain or pain in the side of your back
Symptoms of Urethra or urethral infection:
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Vaginal discharge
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhen to see a doctor?
Discuss with your primary care doctor if you have urine infection symptoms or if any of the symptoms are troubling you. Depending upon the intensity of the symptoms, the doctor may refer you to a urologist. Prescribed antibiotics by a healthcare practitioner can treat most UTIs at home. However, a few serious cases may require hospital admission.
Get the best treatment for your urine infection from our Urologist at Medicover Hospitals.
Causes
The UTI causes include microorganisms, mainly bacteria that pass through the urethra and bladder, thus leading to infection and inflammation. The UTI infection is commonly observed in the bladder but can reach the kidneys too. Usually, the body can get rid of this bacteria, but certain conditions result in UTIs.
Urine infection is more common in women since their urethra is short and close to the anus as compared to men. Bacteria can easily pass through the urinary tract as a result of this. Due to this, women are more susceptible to obtaining an infection after sexual intercourse or while using a diaphragm to prevent pregnancy. A UTI is also more likely with menopause. The majority of bladder infections (cystitis) are caused by E. coli, a kind of bacterium that resides in the intestines.
Risk Factors
- A history of previous UTIs
- Sexual intercourse
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Kidney stones
- Surgery involving the urinary tract
- Bacterial changes that thrive inside the vagina, or vaginal flora. During menopause or the usage of spermicides, results in bacterial changes.
- Age factors, such as older people and young children, are more vulnerable to developing UTIs.
- Poor hygiene in the genital area.
Prevention
It is possible to lower the risk of urinary tract infections by following these steps:
- Drink a lot of water and other liquids.
- Clean the genitals from front to back to prevent the existence of bacteria.
- Immediately after intercourse, empty the bladder to help flush out bacteria.
- Avoid harmful feminine products in the genital area that can irritate the urethra.
- Use safe birth control methods.
Diagnosis of Urinary tract infection
Your healthcare provider will recommend the following diagnostic tests to detect a urinary tract infection.
- Urinalysis or urine test : The urine test will check the urine sample for any infection.
- Urine culture : It is done to find out the type of bacteria in the urine.
- Ultrasound
- Cystoscopy
- CT scan
If the UTI does not respond to medications, or if there is a frequent recurrence of infection, your healthcare provider may suggest the following tests to check for illness in the urinary tract system.
Treatment
When it comes to urinary tract infections, antibiotics are usually the first line of defence. The type of drugs prescribed and the duration depend on the patient's health condition and the results of the diagnostic tests.
For a mild UTI, the doctor may prescribe a shorter course of antibiotic treatment, such as taking the drug for one to three days. For a severe urine infection, intravenous antibiotics may be required in a hospital.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentDos and Don'ts
A UTI or urinary tract infection is a common infection that can affect any part of the urinary tract system. They can be either cystitis or pyelonephritis depending on which part of the urinary tract is affected. Managing UTI requires high level of hygiene and care and a set of dos and don'ts to be followed.
| Drink plenty of liquids | Drink excess of alcohol and caffeine |
| Keep your genital area clean | Ignore cleaning your genitals after sexual activity |
| Use safe birth control methods | Urinate after sexual activity |
| Check for any urinary tract abnormalities | Eat processed, junk foods and citrus fruits like oranges. |
| Wear clean undergarments | Use sprays or powders in the genital area. |
Follow the do's and dont's of urinary tract infection to prevent it or to lessen its severity. By following the precautions as well as taking the complete course of prescribed antibiotics, it is possible to effectively treat the UTI infection and minimize its chances of recurrence.
Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most reliable medical experts,like urologists and general physicians, who plan a personalized treatment pathway for each patient. We believe in a multi-disciplinary approach to managing urinary tract infections that have gone serious or affected other organs as well. However, our treatment plan addresses this condition with precision and bring the best results ensuring continued recovery. We aim to provide the best treatment outcomes and satisfactory patient experiences at a highly affordable cost.
