Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty Doctors in India
In the realm of modern medical advancements, Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) is a pioneering procedure that has revolutionised the treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD). It is commonly known as angioplasty.
PTCA is a minimally invasive intervention designed to alleviate the blockages and restrictions within the coronary arteries. It restores blood flow to the heart muscle, mitigates the symptoms of angina, and potentially prevents heart attacks.
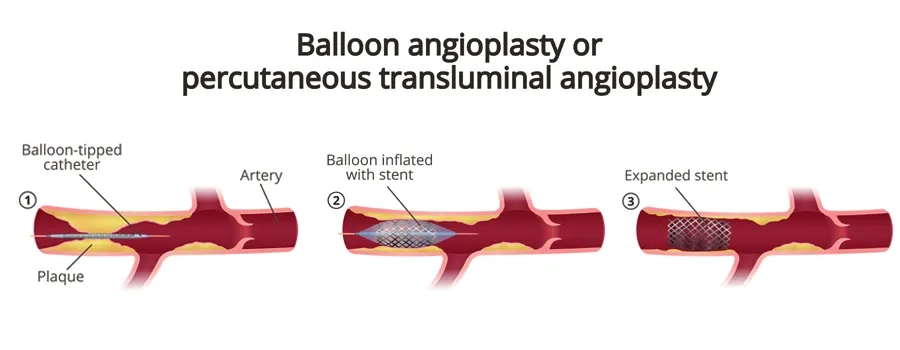
What Steps Are Involved in the PTCA Procedure?
For Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA), medical professionals perform a minimally invasive procedure to treat blocked or narrowed coronary arteries.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of what they do during a PTCA:
-
Patient Assessment: The patient's medical history, physical condition, and diagnostic test results are reviewed to determine the necessity and suitability of PTCA.
-
Preparation: The patient is typically given mild sedation to help them relax during the procedure. The area where the catheter will be inserted (usually the groin or wrist) is cleaned and numbed.
-
Catheter Insertion: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted through a small incision in the chosen artery (femoral or radial artery). The catheter is then carefully threaded through the blood vessels and guided to the coronary arteries using X-ray imaging.
-
Angiography: Once the catheter is positioned in the coronary arteries, a contrast dye is injected through the catheter. This dye highlights the blood vessels on X-ray images, allowing the medical team to visualise the blockages and assess the blood flow.
-
Balloon Inflation: After identifying the blockage, a specialized catheter with a deflated balloon at its tip is advanced to the narrowed area. The balloon is then inflated at the site of the blockage. The inflation compresses the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery and restoring blood flow.
-
Stent Placement (if needed): In some cases, a stent—a tiny mesh-like metallic tube is inserted into the artery along with the balloon catheter. When the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and adheres to the arterial walls, acting as a scaffold to keep the artery open. It prevents the artery from re-narrowing (restenosis) after the balloon is deflated and removed.
-
Balloon Deflation and Catheter Removal: After the artery is widened or a stent is placed, the balloon is deflated, and the catheter is removed. The stent remains in place to help maintain proper blood flow through the previously blocked or narrowed artery.
-
Recovery and Monitoring: After the procedure, the patient is monitored for a short period in a recovery area. Most patients experience relief from angina symptoms as blood flow to the heart muscle improves.
A short hospital stay may be required for observation. Still, the recovery time is significantly shorter compared to open-heart surgeries.
It's important to note that PTCA is a specialized procedure performed by interventional cardiologists who are trained to navigate catheters through blood vessels and perform angioplasty techniques.
PTCA is highly effective for many individuals with coronary artery disease. Still, its suitability depends on the individual's overall health, the complexity of the blockages, and other factors.
How to Recover After PTCA?
Recovery after a Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) procedure is usually relatively quick. Still, it's important to follow your doctor's instructions to ensure a smooth recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
Here's what you can expect and how to manage your recovery:
-
Hospital Stay: Most PTCA procedures are done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can usually go home the same day. In some cases, a short hospital stay might be required for observation, especially if there are complications or if you have other medical conditions.
-
Rest: While you may be able to resume light activities soon after the procedure, it's recommended to rest and take it easy for the first day or two. Avoid activities like heavy lifting during the initial recovery period.
-
Medications: Your doctor will prescribe medications to manage pain, prevent blood clots, and lower the risk of complications. It's important to take these medications exactly as prescribed.
-
Wound Care: If a small incision was made for the procedure, keep the incision site clean and dry to prevent infection. Follow any specific wound care instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
-
Hydration and Diet: Stay well-hydrated and follow a heart-healthy diet. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support your recovery and overall heart health.
-
Medication Management: If you were prescribed new medications or changes were made to your existing ones, make sure to take them consistently. Some of these medications might include antiplatelet drugs, blood thinners, and medications to manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Your doctor will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress, assess the effectiveness of the procedure, and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
-
Gradual Return to Activities: Depending on your circumstances, your doctor will advise when you can resume various activities, including exercise and work. Follow their guidance to avoid straining your body too soon.
-
Lifestyle Changes: PTCA is often a wake-up call to improve one's lifestyle habits. Your doctor may recommend changes such as quitting smoking, improving one's diet, increasing one's physical activity, and managing stress.
-
Symptoms Monitoring: Be vigilant about any unusual symptoms such as a chest pain, shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, or swelling. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
-
Emotional Well-being: It's normal to experience a range of emotions after a medical procedure. If you're feeling anxious, depressed, or overwhelmed, consider talking to a healthcare professional or counsellor.
Lifestyle Changes After PTCA
-
Dietary Changes:
-
Heart-Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (like fish, poultry, beans, and nuts), and healthy fats (such as olive oil and avocados).
-
Limit Sodium: Reduce your intake of salt, as excess sodium can contribute to high blood pressure.
-
Control Portions: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
-
Limit Processed Foods: Minimize your consumption of processed and fast foods, which tend to be high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium.
-
Consult Doctor: Talk to your healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your condition.
-
Aim for Regular Activity: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week.
-
Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises a few times a week to help build muscle and improve overall cardiovascular fitness.
-
Stay Active: Make physical activity a part of your daily routine. Even simple activities like taking the stairs and walking can contribute to your overall health.
-
Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, quitting is one of the most important steps you can take for your heart health. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
-
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of balanced eating and regular physical activity. Excess weight can strain the heart and increase the risk of complications.
-
Stress Management:
- Practice stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing , yoga, or mindfulness.
- Engage in activities you enjoy, spend quality time with loved ones, and find healthy ways to relax.
-
Medication Adherence: These medications help manage risk factors and prevent complications.
-
Regular Medical Checkups: Regular checkups allow your doctor to monitor your progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary.
-
Sleep Well: Aim for quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can negatively impact heart health and overall well-being. Stay Informed:
Educate yourself about heart health, your specific condition, and ways to manage it. Understanding your health empowers you to make better choices.

