What is Piles Surgery?
Pile surgery, or hemorrhoidectomy, is a surgical procedure used to treat severe or recurring haemorrhoids, such as swollen or inflammatory blood vessels in the rectum or anus. Haemorrhoids can cause discomfort, pain, itching, bleeding, and other symptoms.
All these symptoms can negatively influence a person's quality of life. When less invasive therapies fail to relieve the symptoms and improve general well-being, piles surgery becomes an option.
Understanding Piles Surgery
Hemorrhoids are classified into internal and external haemorrhoids based on location. Internal haemorrhoids are located within the rectum, while external haemorrhoids surround the anus.
Pile surgery is typically recommended for cases where haemorrhoids have become enlarged, prolapsed, or are causing severe symptoms.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second Opinion
Steps Involved in the Piles Surgery Procedure
Find the step-by-step piles surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy) surgical procedures for Hemorrhoid Relief
Here's an overview of what happens during piles surgery:
-
Preparation: The patient is positioned on an operating table, and the surgical area is cleaned and sterilized.
-
Anesthesia: The surgery is usually performed under general anaesthesia, ensuring the patient is asleep and pain-free.
-
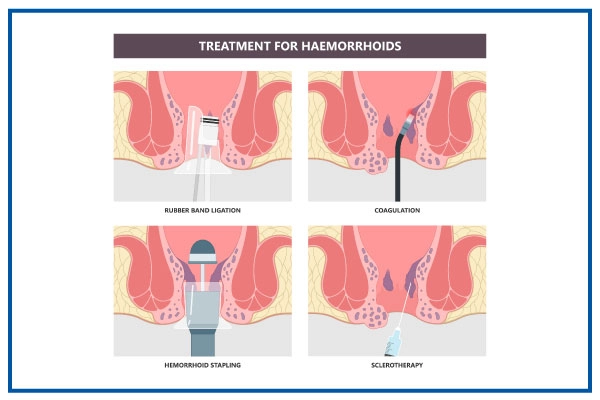
Incision or Excision: The surgeon may choose one of several techniques to remove the haemorrhoids:
-
Excision: The surgeon cuts out the haemorrhoid tissue using a scalpel, scissors, or electrocautery.
-
Stapling: A stapler is used to cut off the blood flow to the hemorrhoidal tissue for internal haemorrhoids, reducing their size.
-
Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation: A technique that involves tying off the arteries supplying blood to the haemorrhoids, causing them to shrink.
-
Laser Surgery: A laser beam vaporizes or removes haemorrhoid tissue.
-
Closure and Dressing: After removing the haemorrhoids, the incision sites are closed using sutures or surgical staples.
- Recovery and Postoperative Care:
- The patient is monitored as they wake up from anaesthesia.
- Pain medication and instructions for wound care are provided.
- A follow-up appointment schedule is usually given.
What are the Indications of Piles Surgery(Hemorrhoidectomy)?
Here are the common indications that might lead to the recommendation of piles surgery:
-
Persistent Symptoms: When haemorrhoids cause persistent symptoms such as pain, itching, bleeding, and discomfort that significantly affect the patient's quality of life, surgery might be considered.
-
Non-Responsive to Non-Surgical Treatments: If over-the-counter treatments, dietary changes, topical medications, and other non-surgical measures fail to alleviate the symptoms, surgery may be recommended.
-
Large or Prolapsed Hemorrhoids: Huge Hemorrhoids, prolapsed (bulging out of the anus) or thrombosed (containing clots) can cause severe pain and discomfort, making surgery a viable option.
-
Chronic Bleeding: If haemorrhoids cause chronic bleeding that leads to anaemia or requires frequent medical intervention, surgery might be necessary to stop the bleeding.
-
Quality of Life Impairment: When haemorrhoids significantly impact a person's daily activities, work, social life, and overall well-being, surgery can offer long-term relief.
-
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids: Thrombosed external haemorrhoids, which are characterized by blood clots forming within the haemorrhoid, can cause intense pain and might require surgical removal.
-
Recurrent Hemorrhoids: If haemorrhoids keep recurring despite previous treatments, surgery might be considered to provide a more lasting solution.
-
Impaired Hygiene and Functionality: Hemorrhoids that interfere with proper hygiene or regular bowel movements due to pain or discomfort could warrant surgical intervention.
-
Severe Bleeding: Hemorrhoids that cause profuse bleeding or bleeding that cannot be managed through conservative methods might necessitate surgery.
-
Patient Choice: In some cases, patients might opt for surgery due to the severity of their symptoms or desire a more definitive solution.
Who Will Treat for Piles Surgery?
Medical professionals involved in treating piles surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy) are those who are experts in the procedure.
Here's an overview of the critical medical professionals involved:
Colorectal Surgeon
- Colorectal surgeons are medical doctors who specialize in the surgical treatment of conditions affecting the colon, rectum, and anus.
- They are trained to perform hemorrhoidectomy and other procedures related to the lower digestive tract.
General Surgeon
-
General surgeons have expertise in performing a wide range of surgical procedures.
- Some general surgeons may also specialize in colorectal surgery and be qualified to perform hemorrhoidectomy.
Proctologist
-
Proctologists, also known as colorectal or pelvic floor surgeons, specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions of the rectum and anus, including haemorrhoids.
Anesthesiologist
-
Anesthesiologists are responsible for administering anaesthesia during the surgery to ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
Surgical Team
- Nurses, surgical assistants, and operating room staff work together as part of the surgical team to assist the surgeon during the procedure.
Gastroenterologist
-
Gastroenterologists are medical doctors who specialize in the digestive system.
- While they often manage non-surgical haemorrhoid treatments, they might refer patients to a colorectal surgeon for surgical intervention.
Steps to Prepare for Piles Surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy)
Preparation for piles surgery involves several essential steps to ensure a successful procedure and smooth recovery. Here's a guide on how to prepare:
Here's an overview of the critical medical professionals involved:
-
Consultation with Specialist: Schedule a consultation with a colorectal surgeon, proctologist, or general surgeon specializing in piles surgery. They will evaluate your condition and medical history and recommend the most suitable treatment plan.
-
Medical Evaluation: Your medical team might conduct additional tests such as blood tests, imaging studies, and possibly a colonoscopy to assess your overall health and the extent of your haemorrhoids.
-
Medication Review: Provide a comprehensive list of all medications you take, including prescription, over-the-counter, and supplements. Some medicines need to be adjusted before surgery.
-
Fasting Instructions: Follow your medical team's fasting instructions before the surgery. You'll be asked to avoid eating or drinking anything for a specific period before the procedure.
-
Anesthesia Discussion: Discuss the type of anaesthesia used during the surgery and any concerns or allergies you might have with the anesthesiologist.
-
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking before the surgery, as smoking can affect healing. Avoid alcohol for a few days before the procedure.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an Appointment
Recovery After Piles Surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy)
Recovery after piles surgery involves a period of healing and adjustment as your body recovers from the surgical procedure. Here's an overview of what to expect during the postoperative phase:
Here's an overview of the critical medical professionals involved:
-
Immediate Postoperative Period: After the surgery, you will be monitored in a recovery area until you wake up from anaesthesia. Your vital signs and comfort level will be closely observed.
-
Hospital Stay: Most piles surgeries are performed outpatient, allowing you to return home the same day. In some cases, an overnight stay might be recommended for observation.
-
Pain Management: Pain is joint after piles surgery. Your doctor will prescribe pain medications to help manage discomfort. Take these medications as directed.
-
Incision Care: Follow your medical team's instructions for incision care and hygiene. Keep the surgical area clean to prevent infection.
-
Diet and Hydration: Eat a balanced and fibre-rich diet to avoid constipation, which can strain the surgical area. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
-
Physical Activity: Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks to allow the surgical area to heal.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Your medical team will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery, assess healing, and remove any sutures or staples if necessary.
-
Bowel Movements: Your doctor might recommend stool softeners or mild laxatives to prevent straining during bowel movements, which can be uncomfortable after surgery.
-
Resuming Daily Activities: You can gradually resume light activities as your healing progresses. Consult your medical team before engaging in more strenuous activities.
-
Pain and Discomfort: Some discomfort is expected during the recovery period. However, contact your medical team promptly if you experience severe pain, excessive bleeding, or other concerning symptoms.
-
Healing Time: Complete healing can take several weeks. The initial discomfort and any swelling or bruising should gradually improve over time.
Lifestyle Changes After Piles Surgery (Hemorrhoidectomy)
After undergoing piles surgery, specific lifestyle changes can contribute to a smoother recovery, promote healing, and reduce the risk of recurrence. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
Here's an overview of the critical medical professionals involved:
-
Hydration and Diet: Consume a fibre-rich diet from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fibre helps prevent constipation and reduces strain during bowel movements. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and maintain soft stools.
-
Avoid Straining: Straining during bowel movements can irritate the surgical area. To make bowel movements more comfortable, use stool softeners or fibre supplements.
-
Regular Bowel Habits: Establish regular bowel habits by visiting the restroom simultaneously each day. Don't ignore the urge to have a bowel movement.
-
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity once your medical team gives you the green light. Exercise improves digestion and helps prevent constipation.
-
Proper Hygiene: After bowel movements, maintain good anal hygiene by gently cleaning the area with mild soap and water. Avoid using rough toilet paper or wipes with alcohol or fragrance.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Avoid sitting or standing for prolonged periods, as this can increase pressure on the anal area. Take breaks and change positions regularly.
-
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking, as smoking can impair healing. Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol can lead to dehydration.
-
Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the abdominal and pelvic areas, which can impact the surgical site.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Continue attending follow-up appointments with your medical team to monitor your healing and address concerns.
-
Avoid Heavy Lifting: Refrain from heavy lifting for several weeks after surgery to prevent strain on the surgical area.
-
Embrace Fiber Supplements: If your diet lacks sufficient fibre, consider using over-the-counter fibre supplements, as your medical team recommends.
-
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body's signals. Consult your medical team if you experience discomfort, bleeding, or any unusual symptoms.